By discovering new ways to manipulate matter at the atomic and molecular levels, advances in nanotechnology are paving the way for innovations in medicine, electronics, materials science and environmental remediation, among many other areas.
An important specialty in this field—and a signature area of study at the University at Albany’s RNA Institute—is DNA nanotechnology, wherein the base pairs that comprise DNA molecules are manipulated to build tiny structures in different shapes that can be used for applications including drug delivery, medical diagnostics and even data storage.
RNA Institute researchers including Postdoctoral Fellow Bharath Raj Madhanagopal and Senior Research Scientist Arun Richard Chandrasekaran, together with a team of UAlbany collaborators, coauthored a new study that explored the unique properties of a certain kind of DNA nanostructure called “switchback DNA” that could have implications for DNA folding in nature and be useful in designing new types of nanostructures with biomedical applications.
Their findings were published in Nature Communications.
Here, Madhanagopal and Chandrasekaran share insights on the fundamentals of their field and the advances that lie in wait with new discoveries in DNA nanotechnology.
What are DNA nanostructures, and why are they important?
Many know DNA as the molecule that stores the genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next. The chemical properties of DNA that make it an excellent molecule for storing genetic information also make it a useful construction material—especially when it comes to making tiny objects, as small as a few nanometers.
The sequences of the four nucleobases in DNA—adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine –are inherently programmable. This is because adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. These reliable patterns in base pairing allow us to design specific strands of DNA that bind together like Lego blocks to form nanostructures.
By using DNA to build nanostructures, we can achieve excellent precision in the size of the structures. We can also make objects of diverse shapes and architectural intricacies—capabilities that are not easily achieved using other technologies. DNA nanostructures are now being developed for use in drug delivery, diagnostics, and data storage, to name a few applications.
What is ‘switchback DNA?’
Just as we use bricks to construct buildings, we use nanometer-sized building blocks called “motifs” and “tiles” made of DNA to create elaborate structures in DNA nanotechnology. Similar to how bricks can come in different shapes and sizes, so can motifs and tiles. Creating these structural motifs and understanding their properties is the foundation of DNA nanotechnology research.
“Switchback DNA” is one of the earliest DNA motifs designed by Nadrian Seeman, the founder of the field of DNA nanotechnology. We wanted to explore how its curious structural features would manifest in nanostructures. By studying the properties of switchback DNA, we believe we can create even more diverse DNA-based nano-objects with exotic properties.
What makes switchback DNA unique?
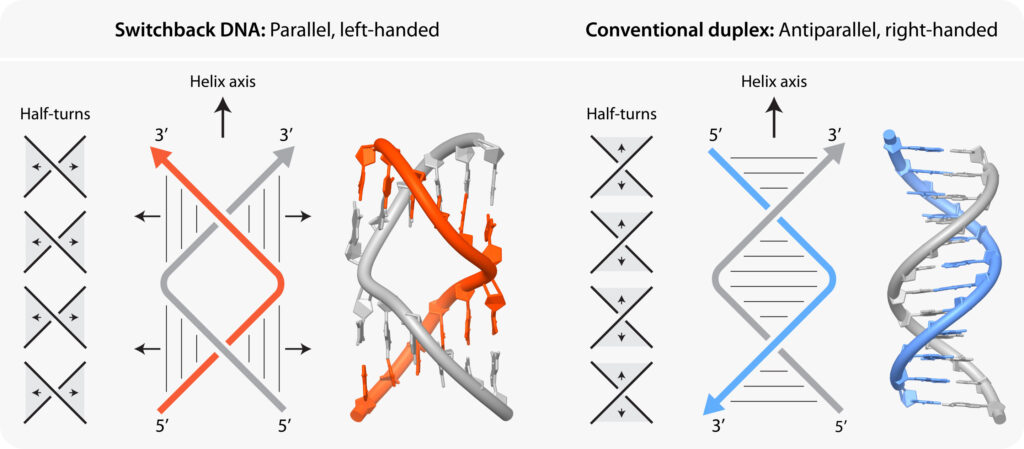
Switchback DNA has only two strands, so it can be directly compared with the double helical structure of DNA that everyone is familiar with. In switchback DNA, the two strands have sections, called half-turns, that resemble normal DNA, but the way they are arranged makes switchback DNA unique.
Typically, DNA is a double helix with right-handed helical sense throughout the molecule. In switchback DNA, right-handed half-turns are arranged in such a way that the molecule as a whole is a left-handed double helix. This is because if you trace the backbone of DNA along the helix, you will find that after every half-turn, the strands fold back. These differences are illustrated in the diagram below.
We have found that switchback DNA’s unique structure can affect properties important to its potential role in biomedical applications—things like structural stability, vulnerability to enzymes, and immunogenic properties, which, for example, can impact the ability of a nanostructure to effectively deliver a drug to a particular tissue. Understanding these properties, and figuring out which can be controlled and how to control them, is critical.
What does the field stand to gain by better understanding switchback DNA?
The results of this study will help researchers who make DNA nanostructures improve their designs using switchback DNA building blocks.
For example, we now know that a common enzyme called “DNase I” does not degrade switchback DNA as quickly as it degrades conventional B-DNA (the DNA that is generally found in living organisms). If we want to use DNA nanostructures to carry drugs to tissues in the body, we don’t want an enzyme to break down the nanostructure before it can reach the target tissue.
If this happened, the drug would not be effective. We can now consider incorporating switchback DNA to help mitigate this challenge, which is a common roadblock in the field.
We also found that there are genetic sequences in the human genome that can potentially fold into switchback DNA. Our results suggest that under some conditions, DNA with specific repeating patterns could form switchback DNA. These sequences are prevalent in the chromosomes of animals and plants, and can adopt structural forms about which we know very little.
It is exciting to know that these sequences can fold into switchback DNA in a test tube under certain conditions. Whether this can happen in a living cell remains to be seen.
Because these repetitive sequences are involved in diseases such as myotonic dystrophy and Huntington’s disease, this avenue of study may help us better understand this class of diseases, and it may also help us discover new drug targets for these diseases in the future.
What are the biggest takeaways from this work?
Our work with switchback DNA shows that we can “tune” the properties of DNA by folding it into different patterns without chemical modifications. Understanding the properties of switchback DNA will be useful in creating DNA devices for biosensing, drug delivery, DNA computation and other applications.
Our findings also demonstrate that the rules of complementarity that Watson and Crick defined in their iconic double-helical model of DNA structure need to be expanded. In the model proposed by Watson and Crick, the directions of the two strands are opposite. That means one end of the first strand interacts with the opposite end of the second strand.
In switchback DNA, the base pairing pattern is different. While most of the rules of complementarity defined by Watson and Crick apply to switchback DNA, the position of the base pairs differs.
Finally, our hypothesis that repeat sequences could form switchback DNA structures opens up interesting discussions—and future studies—on the biological occurrence of such non-traditional DNA structures.