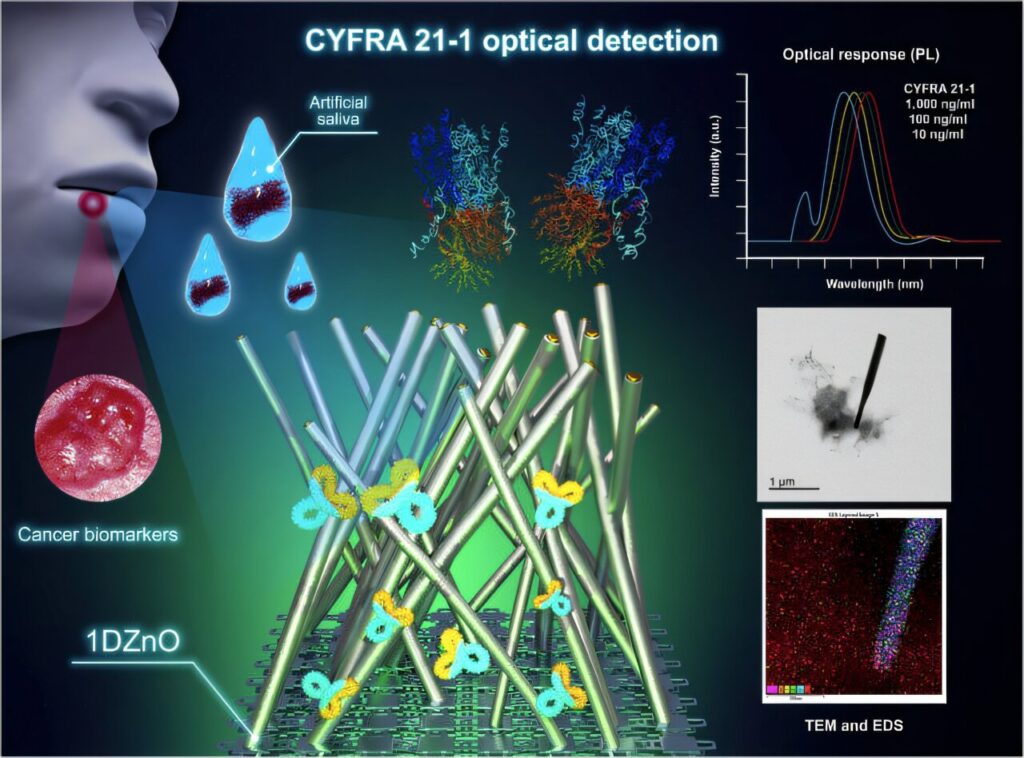
In the ongoing battle against cancer, early detection remains a crucial factor in improving survival rates and reducing the economic burden on health care systems.
A study, published in BME Frontiers, introduces a novel approach to cancer biomarker detection using 1DZnO nanoplatforms. This research, conducted by a collaborative team from the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, presents a promising avenue for the rapid and sensitive detection of CYFRA 21-1, a biomarker associated with various epithelial tumors.
CYFRA 21-1, derived from the cytokeratin 19 fragment, is expressed in the cytoskeleton filaments of epithelial cells and can serve as an indicator for multiple types of cancer, including biliary tract cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, and oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
However, traditional methods of detection, such as imaging and biopsies, often require expensive infrastructure and specialized equipment, limiting their accessibility in low- and middle-income countries.
The research team, led by Dr. Adutt and his colleagues, has developed a physicochemical approach to optical biosensing that leverages the unique properties of 1DZnO nanostructures. These nanostructures exhibit high surface-to-volume ratios, high isoelectric points, and even antimicrobial activity, making them ideal candidates for biosensor development.
The study demonstrates high antibody immobilization efficiencies on 1DZnO nanoplatforms, enabling rapid CYFRA 21-1 testing within a five-minute detection window. Photoluminescence measurements reveal distinct optical responses across different biomarker concentrations, ranging from 10 to 1,000 ng/ml, both in PBS and artificial saliva.
These findings suggest that the developed biosensors have the potential to provide accurate and reliable results in complex matrices, such as saliva, which could facilitate noninvasive and convenient cancer screening.
Furthermore, the research team utilizes advanced microscopic techniques, including transmission electron microscopy (TEM), focused ion beam (FIB) milling, and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), to elucidate the nanoscale interactions between the nanostructures and anti-CYFRA 21-1 antibodies.
These techniques provide insights into the physical and chemical changes that occur during biomarker detection, supporting the observed photoluminescence shifts and intensity changes.
The development of ZnO-based biosensors targeting CYFRA 21-1 represents a significant advancement in cancer detection technology. With its potential for rapid, sensitive, and noninvasive screening, this technology could revolutionize early cancer detection efforts, particularly in resource-limited settings.
As the research team continues to refine and validate their biosensors, the hope is that they will soon become a reality for medical interventions, not only for detection in sick patients but also for early cancer screening in healthy populations.
Provided by
BMEF (BME Frontiers)