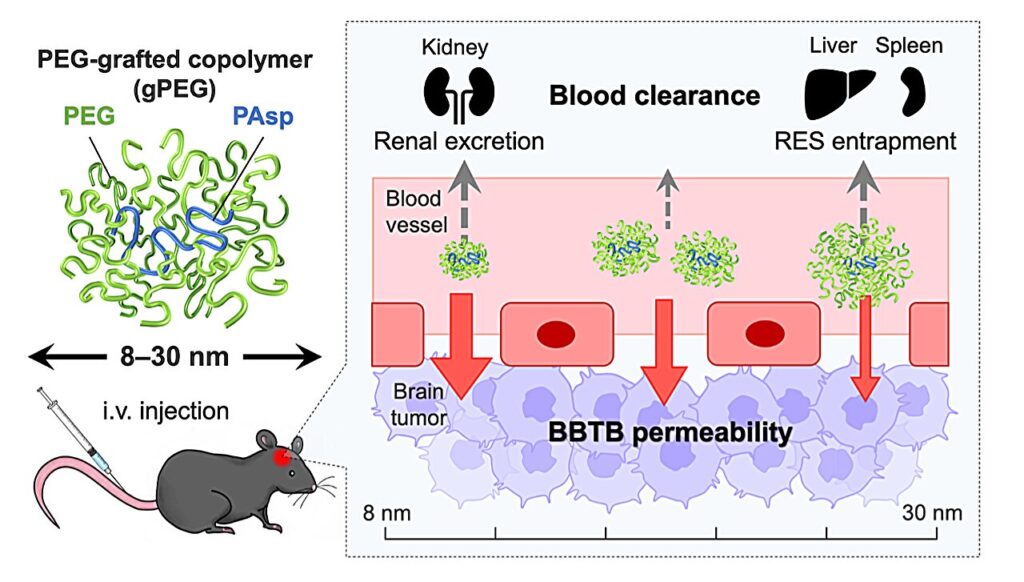
Currently, there is no effective treatment for glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the most frequent and malignant type of brain tumor. Some low molecular weight antitumor agents are used to permeate the gaps between endothelial cells in the BBTB (blood−brain tumor barrier), which is a characteristic blood vessel structure and formed by the partial collapse of the blood−brain barrier, but they are rapidly excreted from the kidneys, resulting in low GBM accumulation.
Additionally, their nonspecific distribution in healthy tissues often induces severe side effects such as myelosuppression and immunosuppression. It is known that 30−100 nm-sized nanomedicines avoid rapid renal excretion and increase drug accumulation efficiency in some tumor models. However, the GBM accumulation level of such nanomedicines remains limited, presumably because of the relatively low blood vessel permeability in the BBTB.
Now, the Innovation Center of NanoMedicine (iCONM) has announced with the Graduate School of Engineering of The University of Tokyo that a group led by Prof. Kanjiro Miyata, Visiting Scientist of iCONM (Professor, Department of Materials Engineering, The University of Tokyo), has found that the threshold for tissue permeability of brain tumors is in the range of 10−30 nm, using a nanoruler, which is a biocompatible polymer used for measurement of gaps in the body.
In particular, when the size of the nanoruler is adjusted to 10 nm, it achieves an unprecedentedly high brain tumor accumulation. Obtained results have provided significant guidance for the design of future brain tumor nanomedicine.
Miyata and the team studied size-dependent GBM targetability using a size-tunable stealth polymer, termed a “polymeric nanoruler,” and reported the results in the journal Bioconjugate Chemistry.
Small gPEGs exhibited efficient brain tumor accumulation, with 10 nm of gPEGs achieving the highest accumulation level (19 times higher than that in the normal brain region and 4.2 times higher than that of 30 nm of gPEGs), presumably because of the optimal size associated with enhanced BBTB permeability and prolonged blood circulation.
In conclusion, this study explored the size effect of nanomedicine on passive GBM targeting with size-tunable poly(ethylene glycol)-grafted copolymers (gPEGs) as polymeric nanorulers (ranging from 8.5 to 30 nm).
Miyata will report on the drug conjugation and optimization for the enhanced GBM-targeted drug delivery in future work. Overall, this study provides a useful molecular design to develop GBM-targeted nanomedicines for chemotherapy, radiation therapy, photodynamic/thermal therapy, and diagnostics.
Provided by
Innovation Center of NanoMedicine