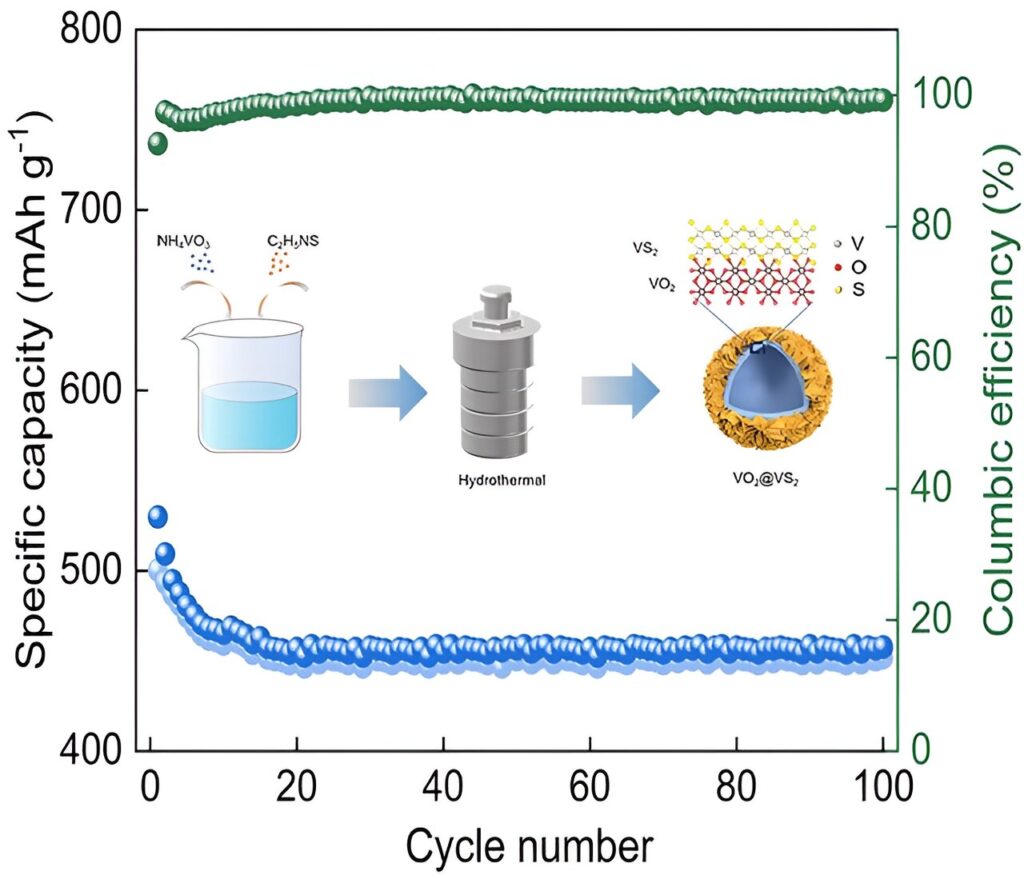
Researchers from Qingdao University have synthesized VO2@VS2 hollow nanospheres using a one-step hydrothermal process, creating a highly efficient cathode material for zinc-ion batteries. This powerful heterostructure significantly enhances battery performance, delivering a reversible capacity of 468 mAh g−1 and maintaining 85% retention after 1,000 cycles.
The nanomaterial’s unique architecture facilitates faster Zn-ion transport, enhanced electrochemical stability, and longer cycle life, offering a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This advancement paves the way for more efficient, safer, and environmentally friendly energy storage systems crucial for applications like electric vehicles and grid storage.
The work is published in the journal Materials Futures.
Zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) are a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries in advanced energy storage systems due to their safety, cost, and environmental friendliness. For large-scale energy storage applications like electric vehicles and grid storage, zinc is abundant, non-toxic, and can operate in aqueous electrolytes. However, the cathode material greatly affects ZIBs’ capacity, rate capability, and cycle life.
Vanadium dioxide (VO2) is a popular ZIB cathode material due to its high theoretical capacity and zinc-ion insertion/extraction. However, VO2 suffers from low electrical conductivity and poor performance rate, limiting its practical application in high-performance batteries. This limitation can be overcome by combing VO2 with highly conductive materials like vanadium disulfide (VS2).
VS2 offers several advantages, including a layered structure with wide interlayer spacing, facilitating rapid zinc-ion diffusion, and excellent electrical conductivity. The combination of VO2 and VS2 not only enhances the electronic conductivity and Zn-ion insertion/extraction capabilities, but also improves structural stability during long-term cycling. The heterogeneous VO2/VS2 interface provides sufficient active sites and modulates the electronic structure, enabling high Zn-ion storage capacity dominated by pseudocapacitance behavior.
Theoretical analysis further underscores the promising Zn-ion reaction dynamics of VO2@VS2, positioning it as a strong candidate for high-capacity Zn-ion batteries with potential applications in practical energy storage systems.
Despite the promising electrochemical performance of VO2@VS2 hollow nanospheres, further improvements are needed to address potential challenges. One direction is to optimize the heterointerface structure to enhance Zn-ion diffusion and charge transfer kinetics. Additionally, doping strategies can be explored to improve the structural stability and cycling durability of the material. These advancements will pave the way for VO2@VS2 to become a more viable candidate for high-performance aqueous Zn-ion batteries.
By combining one-step hydrothermal synthesis with detailed electrochemical analysis, VO2@VS2 hollow nanospheres emerged as extremely promising cathode materials for Zn-ion batteries. This study provides a versatile interfacial heterostructure strategy that can significantly improve charge transfer, Zn-ion storage and cycling stability. This research summarizes the potential of VO2@VS2 as a high-performance, environmentally friendly cathode for Zn-ion batteries in next-generation energy storage applications.
Provided by
Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory