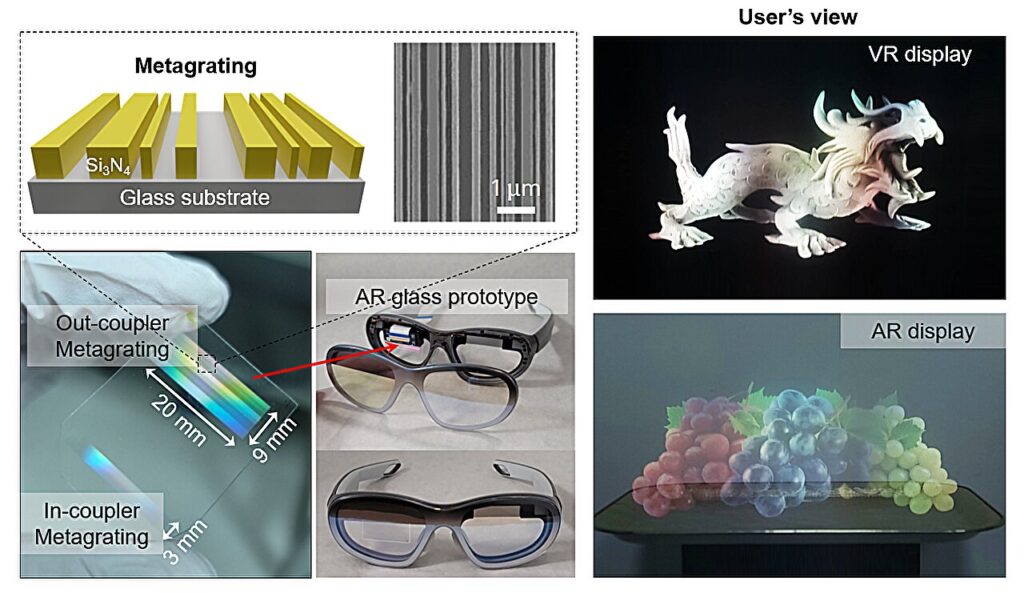
Augmented-reality (AR) technology is rapidly finding its way into everyday life, from education and health care to gaming and entertainment. However, the core AR device remains bulky and heavy, making prolonged wear uncomfortable. A breakthrough from POSTECH now promises to change that.
The study is published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
One of the main hurdles to the commercialization of AR glasses has been the waveguide. In AR optics, the lens itself also serves as a “highway of light,” guiding virtual images directly to the user’s eye. Due to chromatic dispersion, conventional designs have required separate waveguide layers for red, green, and blue light—three to six stacked glass sheets—inevitably increasing both weight and thickness.
Professor Junsuk Rho and colleagues at POSTECH have eliminated the need for multiple layers by developing an achromatic metagrating that handles all colors in a single glass layer. The key is an array of nanoscale silicon-nitride (Si3N4) pillars whose geometry was finely tuned by a stochastic topology-optimization algorithm to steer light with maximum efficiency.

In experiments, the researchers produced vivid full-color images using a 500-µm-thick single-layer waveguide—about one-hundredth the diameter of a human hair. They also secured a comfortable 9-mm eyebox, ensuring images remain sharp even if the viewer’s eye shifts slightly.
The new design erases color blur while outperforming multilayer optics in brightness and color uniformity. Once commercialized, this technology could make AR glasses as thin and light as ordinary eyewear, reducing wearer fatigue and trimming manufacturing costs thanks to a simpler process. The era of truly everyday AR is a step closer.
“This work marks a key milestone for next-generation AR displays,” said Prof. Rho. “Coupled with scalable, large-area fabrication, it brings commercialization within reach.”
The study, authored by Junsuk Rho (corresponding author, POSTECH), Seokwoo Kim, Joohoon Kim, and Seokil Moon, was carried out by POSTECH’s Departments of Mechanical, Chemical and Electrical Engineering and the Graduate School of Interdisciplinary Bioscience & Bioengineering, in collaboration with the Visual Team at Samsung Research.