RNA interference (RNAi) technology has gradually become a cutting-edge technology for treating diseases such as genetic disorders and cancer due to its huge potential in gene expression regulation. However, the efficient delivery and safety of short interfering RNA (siRNA) remain key challenges for its clinical application.
Exosomes, as natural nanoscale extracellular vesicles, have gradually become a research hotspot for optimizing siRNA delivery due to their excellent biocompatibility, stability, long-lasting in vivo circulation time, and precise tissue targeting ability. However, traditional exosome delivery mainly relies on endocytosis, which leads to rapid degradation of RNA molecules in lysosomes, thereby limiting delivery efficiency.
In a study published in Nature Nanotechnology, a research team led by Gan Yong and Yu Miaorong from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Hu Guoqing’ group from Zhejiang University, combining theoretical modeling with experimental studies, revealed the key role of cholesterol in regulating delivery of RNA drugs by exosomes, and the underlying mechanism.
Using a controllable membrane engineering strategy, researchers prepared exosomes with different cholesterol contents, such as milk exosomes, ginger exosomes, and tumor cell-derived exosomes. Using technologies like transmission electron microscopy, they comprehensively characterized the cellular uptake behavior of these exosomes.
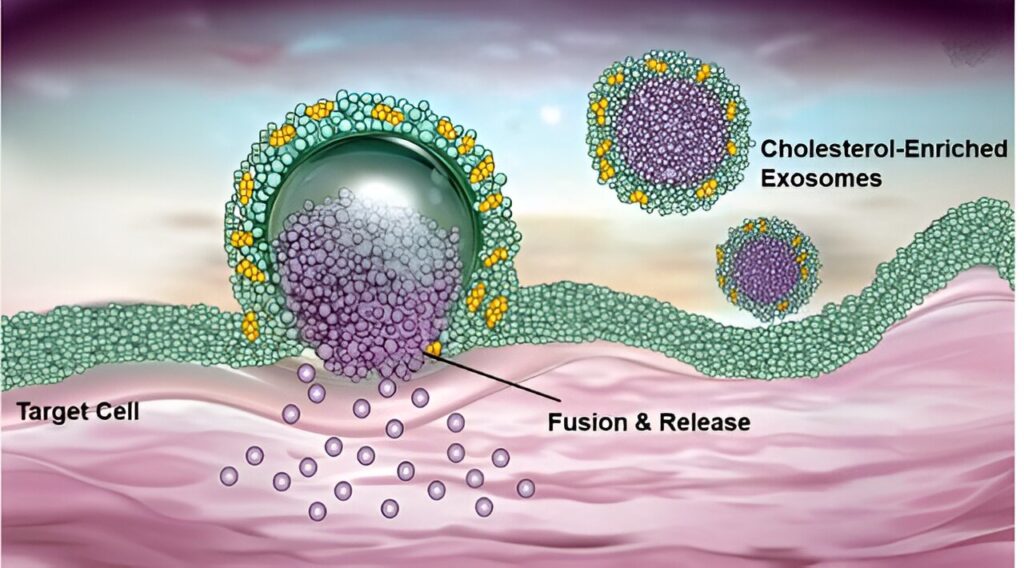
The results showed that increasing cholesterol content in the exosome membrane significantly enhanced its interaction with the target cell membrane, promoting exosome entry into the cell through membrane fusion rather than endocytosis, thus bypassing the limitation of lysosomal degradation.
Molecular models also revealed that cholesterol-rich exosomes exhibited stronger membrane deformability and could expand their contact area with the cell membrane, thereby delivering siRNA directly to the cytoplasm with high efficiency through a membrane fusion mechanism.
In the in vitro experiment, milk exosomes enriched in 30% cholesterol (30%Chol/MEs) successfully delivered PLK1 siRNA, significantly down-regulated PLK1 mRNA and protein expression levels, and induced apoptosis of tumor cells. The effect was significantly better than that of traditional transfection agents Lipo 2000 and RNAiMAX.
The in vivo experiment further confirmed that 30% Chol/MEs/siPLK1 could effectively inhibit tumor growth in the mouse colorectal tumor model through both oral and intravenous injection, indicating that these special exosomes have great potential as gene therapy vectors.
In summary, the successful modulation of cholesterol content in exosome membranes to promote membrane fusion-mediated cargo transfer offers exciting opportunities for the development of safer and more efficient gene therapy strategies.