An article published in the Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering describes a possible strategy for promoting selective inhibition of multidrug-resistant bacteria, which are increasingly abundant owing to the indiscriminate use of antibiotics and are therefore a major human health hazard.
The article proposes to use nanoparticles of metal or metal oxide to inactivate multiresistant bacteria by means of ion release, direct contact between the nanoparticles and the bacteria via electrostatic interaction, or formation of reactive oxygen species. All these processes kill the bacteria by disrupting their cell membranes.
The authors include Brazilian scientists affiliated with the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF), a Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar); the University of São Paulo’s São Carlos Institute of Physics (IFSC-USP); São Paulo State University’s Institute of Chemistry (IQ-UNESP); and the Maranhão Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology (IFMA).
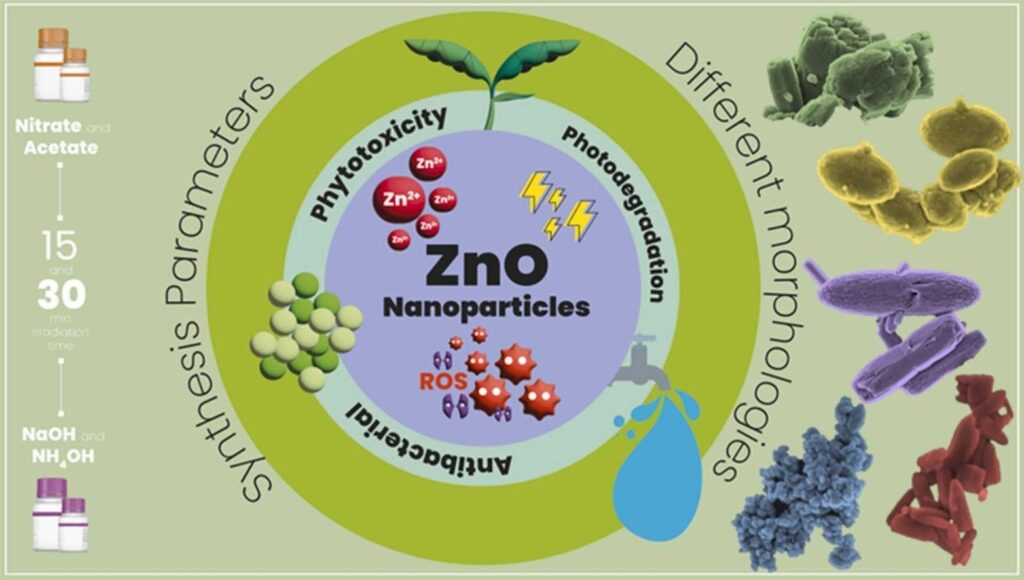
The researchers produced a number of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) with varying morphologies and tested them in an aqueous medium, finding that the nanomaterial successfully killed a large group of multiresistant bacteria isolated from human clinical specimens. The aim of the experiment was to verify the antibacterial activity of the ZnO NPs against strains from clinical isolates.
Principal component analysis, a statistical procedure that summarizes the information content in large data tables, was used to investigate how changes to nanoparticle synthesis parameters influenced the material’s antibacterial activity.
According to Gleison Marques, a Ph.D. candidate in chemistry at UFSCar and first author of the article, the advantage of using ZnO is that it is considered safe by regulatory authorities worldwide and can be used in many types of material functionalized for mass production. In addition, ZnO NPs are cheaper than nanoparticles made of other metals, such as gold or silver.
The material has the potential to be used in water treatment, food packaging and sunscreen, among other applications, Marques said, but more studies are needed to analyze possible contraindications regarding dosage, toxicity in water, and interaction with complex biological systems.
“Next steps include application of these nanoparticles in polymer systems to produce nanocomposites that can be used to coat metal surfaces in hospital environments, for example,” he said.