A research group led by Prof. Yang Liangbao from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has enhanced localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) by studying Cu₂O₁₋ₓ superlattices with oxygen vacancies, providing new insights into vacancy doping in semiconductors and LSPR induction in metal oxide nanoparticles. The findings are published in Nano Letters.
LSPR refers to the collective oscillation of free electrons in metal nanoparticles, which results in a resonance phenomenon that absorbs and scatters light at specific wavelengths. This unique optical property enables LSPR to be applied in various fields such as biosensing, where it enhances detection sensitivity, and in photocatalysis, where it facilitates light-driven chemical reactions. Additionally, LSPR-based materials show promise in color tuning and energy harvesting applications.
The researchers have long focused on the study of LSPR enhancement. Building on this foundation, they advanced their research by investigating the potential of Cu₂O₁₋ₓ superlattices to enhance LSPR effects.
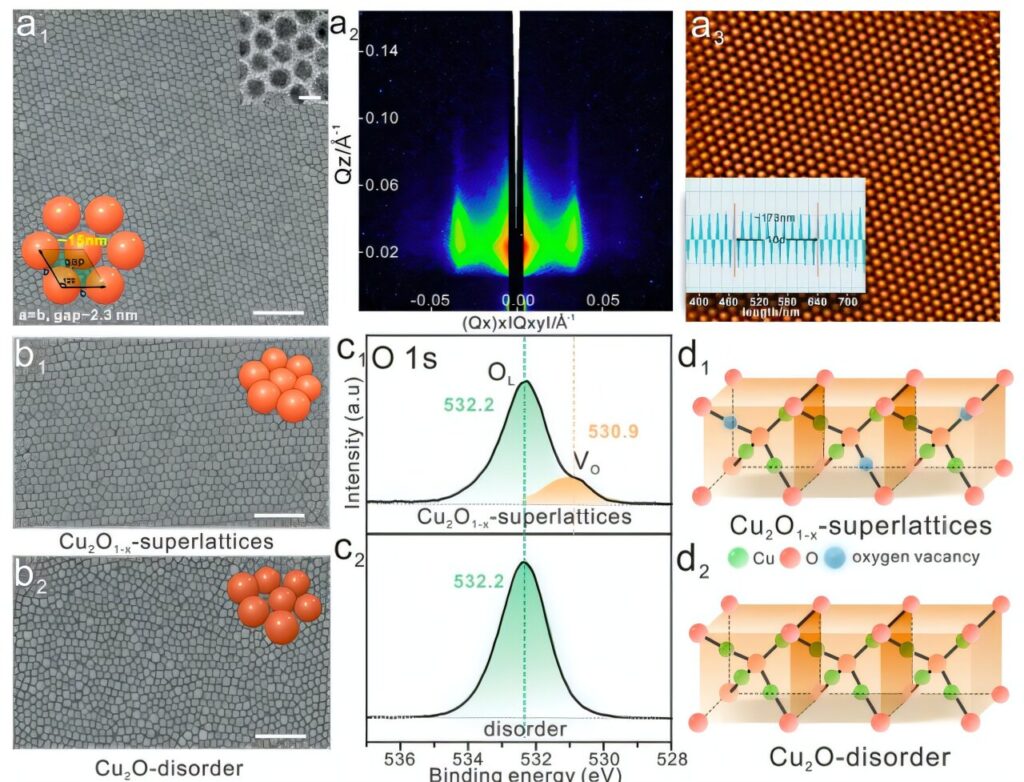
Through a series of carefully designed experiments, they successfully synthesized Cu₂O₁₋ₓ superlattice structures that were rich in oxygen vacancies, and observed a remarkable enhancement of LSPR.
They showed that these oxygen vacancies play a crucial role in increasing the carrier concentration and modifying the electronic band structure of the material.

Specifically, the oxygen vacancies caused the valence band edge to shift closer to the Fermi level, while narrowing the band gap. This structural alteration induced intraband transitions that generated strong LSPR modes and significantly enhanced the electromagnetic field.
As a result, the material showed excellent performance in surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy detection.
This study provides a novel perspective on vacancy doping in semiconductors and opens new avenues for inducing LSPR in metal oxide nanoparticles.