Queen Mary University of London researchers have developed new nanocomposite films using starch instead of petroleum-based materials, marking a significant advancement in the field of sustainable electronics.
The study, published in Advanced Functional Materials, showcases the development of biodegradable, flexible, and electrically conductive materials that hold promise for a wide array of electronic and sensing applications.
These starch nanocomposites offer tunable mechanical and electrical properties, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to petroleum-based materials.
With a growing global need for sustainable solutions in electronics, this breakthrough presents a major step toward reducing e-waste and promoting eco-friendly electronics. The new nanocomposite films are made from starch, one of the most abundant natural polymers found in plants such as potato, maize, pea and corn, and MXene, a highly conductive 2D material that is manufactured in-house. These films can be tailored for various uses, such as monitoring human body movement, tactile sensing, and electronic smart skins.
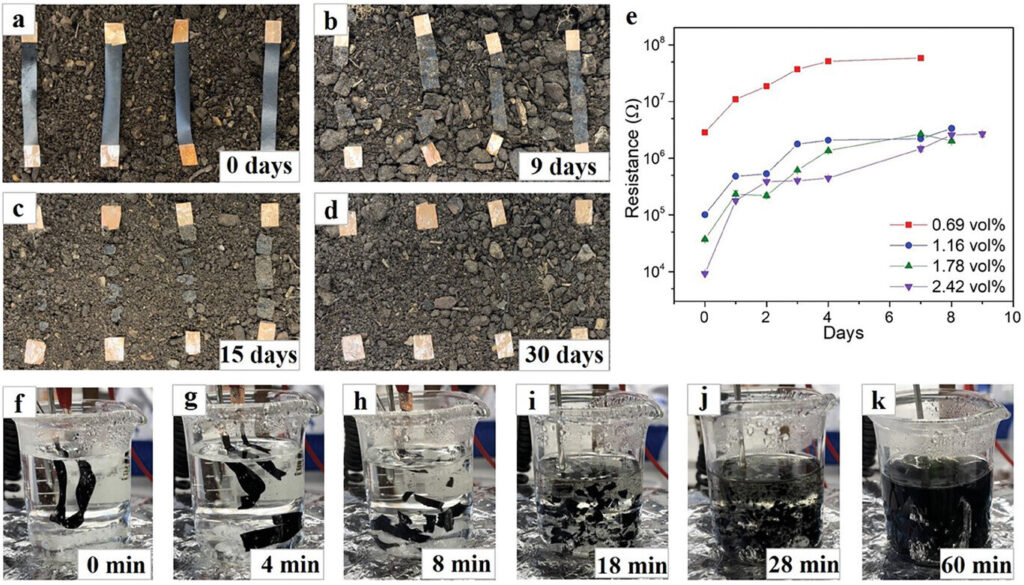
A key innovation towards sustainable electronics is the fact that the starch-based films decompose within a month when buried in soil, offering a rapid degradation process that contrasts sharply with conventional non-degradable plastics.
Additionally, by adjusting MXene concentrations, researchers achieved precise control over the films’ mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, and sensing capabilities. This allows for customized applications across different industries, from health care to wearable electronics. These composites use natural, abundant materials, with a production process reliant on water as a solvent, further enhancing their sustainability credentials.
Lead researcher Ming Dong, from QMUL’s School of Engineering and Materials Science, said, “Our findings have shown that sustainable electronics can be achieved through these starch-based nanocomposites, offering not just an environmentally friendly solution but also practical applications in flexible electronics.”
A path toward green electronics
Dimitrios Papageorgiou, lead academic and corresponding author of the study, said, “This work represents a significant leap forward in addressing the global challenge of e-waste. By using abundant and biodegradable materials, we are opening up new avenues for sustainable electronics. These starch-based composites offer a solution that merges environmental responsibility with high-performance sensing and electronics capabilities.”
The research team believes these developments can lead to a future where electronic devices are no longer part of the environmental burden but contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.