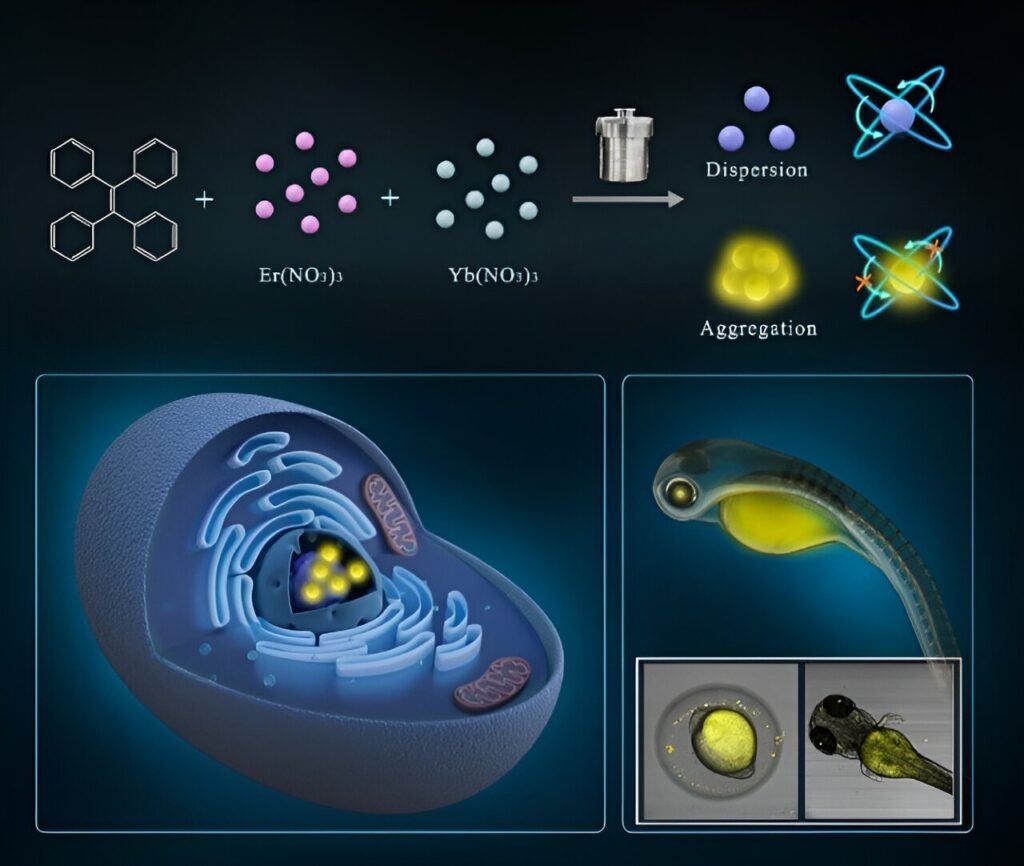
Carbon dots (CDs) are an intriguing class of nanomaterials that have attracted a great deal of attention in recent years. These carbon-based materials possess excellent fluorescence properties, making them highly appealing for a wide range of applications.
Researchers at the Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Technology (SIBET) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently developed novel aggregation-induced emission (AIE) carbon dots (Y-CDs) for cellular imaging.
Results of this study were published in Materials & Design, titled “Rare earth-modified yellow carbon dots for long-term imaging in cells and zebrafish.”
Despite their excellent properties, CDs are often limited by aggregation-induced quenching effects. In the solid or aggregated state, the fluorescence of CDs significantly decreases or even disappears, which has limited the development and application of CDs.
In this study, Dong Wenfei and his team of SIBET synthesized a novel AIE CDs by introducing rare earth elements (Yb and Er), called Y-CDs. Y-CDs exhibited excellent optical properties, including excitation-independent emission, pH-responsive and temperature-sensitive properties. “They were found to have low requirements in terms of incubation time, and could achieve good imaging effect when the incubation concentration was low,” said Dong.
Y-CDs showed excellent nuclear targeting ability in HeLa cells. In zebrafish and zebrafish embryos, Y-CDs showed biocompatibility and safety in long-term imaging experiments, and enabled selective visualization of the crystalline and digestive systems of the zebrafish.
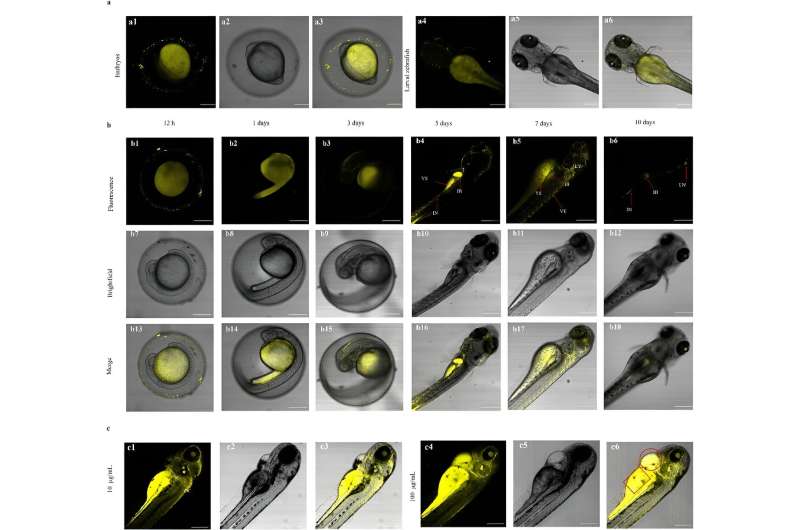
This study proves that Y-CDs can effectively penetrate zebrafish and zebrafish embryos and also have tissue affinity for juveniles, which provides a novel material choice for zebrafish imaging, according to Kou Xinyue, first author of the study.
The synthesized rare earth Y-CDs show great promise for a variety of imaging and biological sensing applications. Further research and development in this area could lead to the advancement of bioimaging techniques and the exploration of new applications in biology and medicine.