Nanoscience explores the ultrasmall scale, interfacing with multiple scientific disciplines to foster innovations in technology, energy, and medicine. By manipulating atoms and molecules, it promises a vast array of applications, from green technologies to treatments for brain disorders. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
What Is Nanoscience?
Nanoscience is the science of the incredibly small — sizes that only the most high-tech of high-tech microscopes can see. It is one of the hottest topics in all of science, touching on physics, biology, chemistry, geology, and materials science and engineering. By working in the world of the ultrasmall, scientists are bringing big new things to our world. These include new green technologies, treatments for various diseases, energy technologies, and more.
The term “nano” means one billionth of something. The “nano” in nanoscience refers to a nanometer, one-billionth of a meter (1 meter = 3.3 feet). Just how small is that?
In this Science 101: What is Nanoscience video, assistant scientist Jie Xu explains what nanoscience is, and how it is being applied at Argonne’s Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM), a Department of Energy Office of Science User Facility. Nanoscience is the science of the incredibly small — sizes that only the most sophisticated high-tech microscopes can see. It is one of the hottest topics in all of science. Every year, many hundreds of scientists travel to the CNM from around the world to investigate the properties of materials at the scale of atoms and molecules. By advancing our understanding of material structure at this scale, Argonne scientists like Xu and many others are gaining ever deeper understanding of properties at the nanoscale and how they can be put to practical use. Armed with that knowledge, they are designing and building the next generation of materials. These are leading to sustainable green technologies, more efficient mass-manufacturing, new drugs, innovative treatment of brain disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, improved battery materials, better electronic devices, and more.
Let’s pretend you are in the world of Alice in Wonderland and stumble on a magic potion in a bottle marked DRINK ME. You take one sip and shrink by 1500 times. You are now a millimeter in size, the height of a small raindrop. Curious, you take another sip from the magic potion and shrink by a factor of a thousand. Being a micrometer in size now, you are about the size of the bacteria floating around in a raindrop. You take another sip and shrink another factor of a thousand. Having reached the nanometer size, you are now only about three times larger than a single molecule of water, which consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen. In a single raindrop, there are over one-sextillion molecules of water. A sextillion is the number one followed by twenty-one zeroes!
Science at this ultrasmall scale is reaping many benefits for society because all materials are made of atoms and molecules. And the same atoms and molecules combined in different ways can yield an endless bounty of properties. They can be made to be softer or stronger, conduct heat or electricity better, reflect light differently, and so on.
At Argonne National Laboratory, the Center for Nanoscale Materials (CNM) is one of five Department of Energy centers in the U.S. for nanoscience and technology.
By advancing our understanding of materials, molecules and chemical processes at this scale, scientists at these centers are gaining ever deeper understanding of how properties emerge that can be put to practical use. Armed with that knowledge, they are designing and building the next generation of materials and molecules. These are leading to sustainable green technologies, more efficient mass-manufacturing, new drugs, treatment of brain disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, improved battery materials, new quantum information and sensing devices and more.
Credit: Argonne National Laboratory
What Are NanoStructures?
Structures only the most high-tech of microscopes can see.
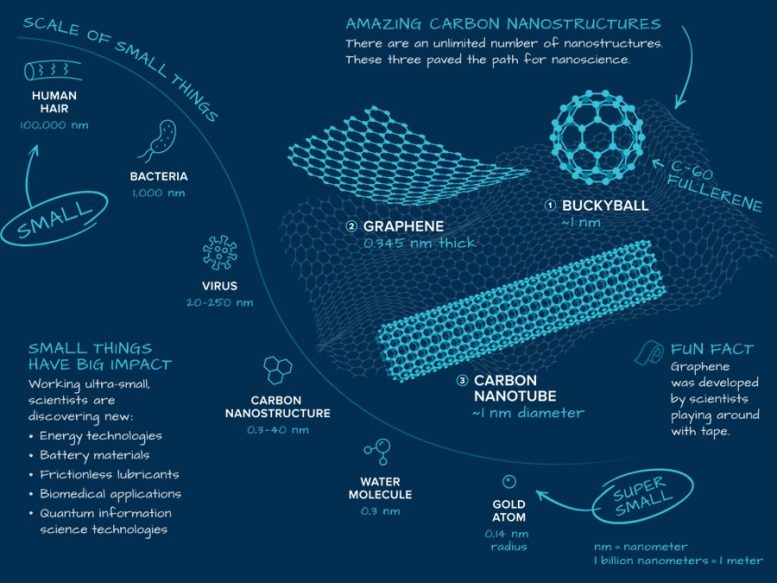
Nanostructures have one or more dimensions a hundred-thousand times smaller than the thickness of a human hair and not much larger than a gold atom or water molecule. There are countless varieties of nanostructures. Interest in them exploded with the discovery of buckyballs in the 1980s, followed by two related structures.
- BUCKYBALL Named after architect Buckminster Fuller, it consists of sixty carbon atoms joined in a soccer-ball shape. Its synthesis led to the invention of carbon nanotubes and graphene.
- GRAPHENE This nanomaterial is a flat sheet of carbon atoms less than a nanometer thick. Despite its ultra-thinness, graphene is 200× stronger than steel.
- CARBON NANOTUBE Scientists can roll up graphene to form nanotubes. This shape is attractive for many applications, such as creating ultra-strong fibers and fabrics. It can also be used as an additive to strengthen aerospace vehicle.


