Oxidative redispersion at elevated temperatures has long been utilized in heterogeneous catalysis for the regeneration of sintered metal catalysts and the synthesis of metal single atom and cluster catalysts. These redispersion processes require a considerable energy input. Therefore, the quest for eco-friendly and energy-saving redispersion strategies remains an urgent priority.
A research group led by Fu Qiang from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has revealed the water-assisted oxidative redispersion of Cu particles through the formation of Cu hydroxide at room temperature (RT). The study was published in Nature Communications.
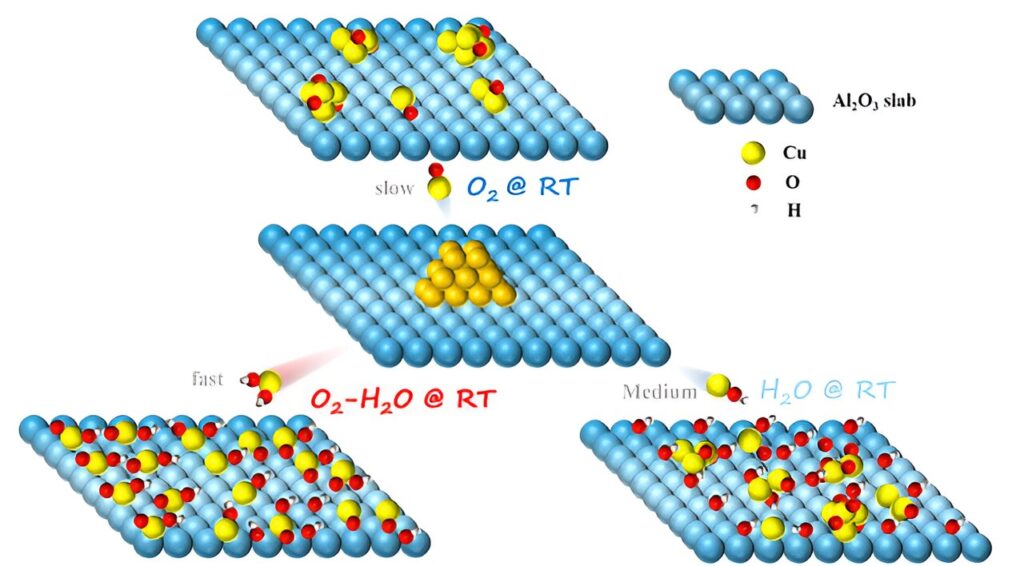
The researchers discovered that Cu nanoparticles supported on the surface of γ-Al2O3 could spontaneously redisperse at RT. They verified that the hydroxylation of the support surface in a moist environment and the formation of Cu-OH species were the key factors driving RT redispersion of Cu nanoparticles on γ-Al2O3 surfaces. The O2 and H2O led to the formation of hydroxylated Cu species, accelerating the diffusion of Cu atoms on the γ-Al2O3 surface.
In addition, most support surfaces, such as γ-Al2O3, SiO2, and CeO2, could undergo hydroxylation in a moist atmosphere to form abundant surface OH groups that captured migrating Cu species.
The “push” (migration) and “pull” (anchoring) effects of gaseous H2O facilitated the structural transformation of Cu species from Cu nanoparticles to Cu single atoms at RT, thereby enhancing their catalytic activity in the reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) and preferential oxidation of carbon monoxide (CO-PROX) reaction.
This study highlighted the significant role of H2O in the dynamic structural evolution of supported metal nanocatalysts and developed a simple strategy for the redispersion of sintered Cu-based catalysts at RT using O2-H2O treatment, avoiding the energy consumption of traditional high-temperature regeneration processes.
“Water widely exists in heterogeneous catalysis, and the effect of water in the dynamic structure evolution of supported metal nanocatalysts cannot be ignored. More attention should be paid to possible metal redispersion/sintering in water-containing conditions,” said Prof. Fu.