A research team collaborated to identify the principle of an eco-friendly energy-based soft mechanoluminescent complex that emits light without batteries. It is expected to be applied in various fields, such as optical sensors, artificial skin, and displays. The team includes Dr. Jeong Soon-moon, Dr. Lim Sung-jun (Division of Nanotechnology) and Prof. Kim Young-hoon (Department of Applied Chemistry, Kookmin University).
The findings are published in the journal Small.
Mechanoluminescent material is a material that emits light in response to pressure or mechanical stress. When triggering light emission in conventional mechanoluminescent materials, significant pressure must be applied, and additional processing, such as energization with ultraviolet or blue light, is required for repeated emission.
In 2013, the research team reported to the academic community a complex based on transparent silicone rubber and a luminescent material that generates soft but strong mechanoluminescence. In particular, the soft mechanoluminescent complex can emit bright light even under slight pressure or mechanical stress, and it can generate light continuously without preprocessing, enabling its utilization in various industrial fields.
For the past decade, efforts have been made by academia to incorporate the complex into various applications, but the source of light emission has not been clearly identified, limiting the development of new materials and application technologies.
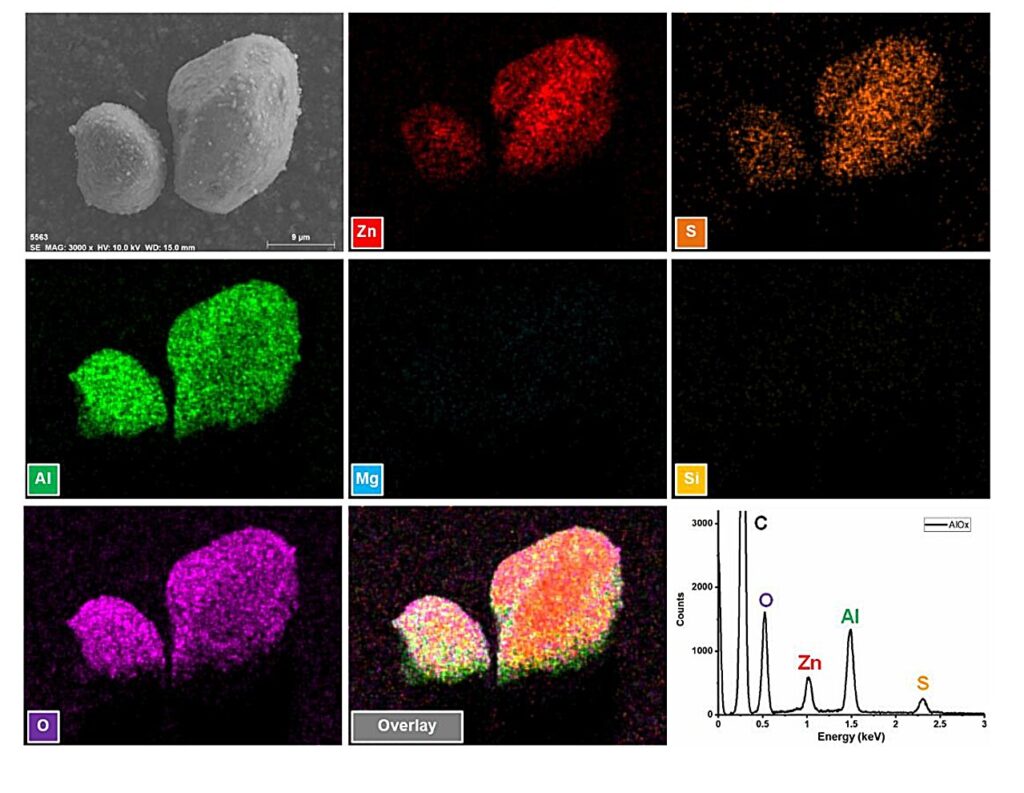
The research team performed various analyses on the phosphor to uncover the principle of the soft mechanoluminescent complex. They observed that the phosphor exhibited strong mechanoluminescence when coated with amorphous aluminum oxide externally. The aluminum oxide was found to generate strong electricity through friction with the flexible transparent silicone rubber, and the electricity was found to activate zinc sulfide luminescent particles.
In their experiments, the research team used silicon oxide, magnesium oxide coating, and polyurethane polymer to control the magnitude of triboelectricity. Consequently, the magnitude of triboelectricity was found to be related to the brightness of mechanoluminescence, which was verified via experiments and simulations. Based on the finding, the team proposed a new interfacial triboelectricity-based alternating current electroluminescence model to identify the mechanoluminescence phenomenon.
“It is highly significant that we have completed the final proof-of-principle of our previously published results,” said Dr. Jeong Soon-moon of the Division of Energy & Environmental Technology.
“We hope that this will enable the development of brighter mechanoluminescence complexes that demand less power, and ultimately, contribute to the expansion of the field by creating new applications of mechanoluminescence.”
Provided by
DGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology)