SMU nanotechnology expert MinJun Kim helped a team of researchers at The University of Texas at Austin to develop a less expensive way to detect nuclease digestion—one of the critical steps in many nucleic acid sensing applications, such as those used to identify COVID-19.
Nucleic acid detection is the primary method for identifying pathogens that cause infectious diseases. As millions of PCR tests were run worldwide every day during the COVID-19 pandemic, it is important to reduce the costs of these tests.
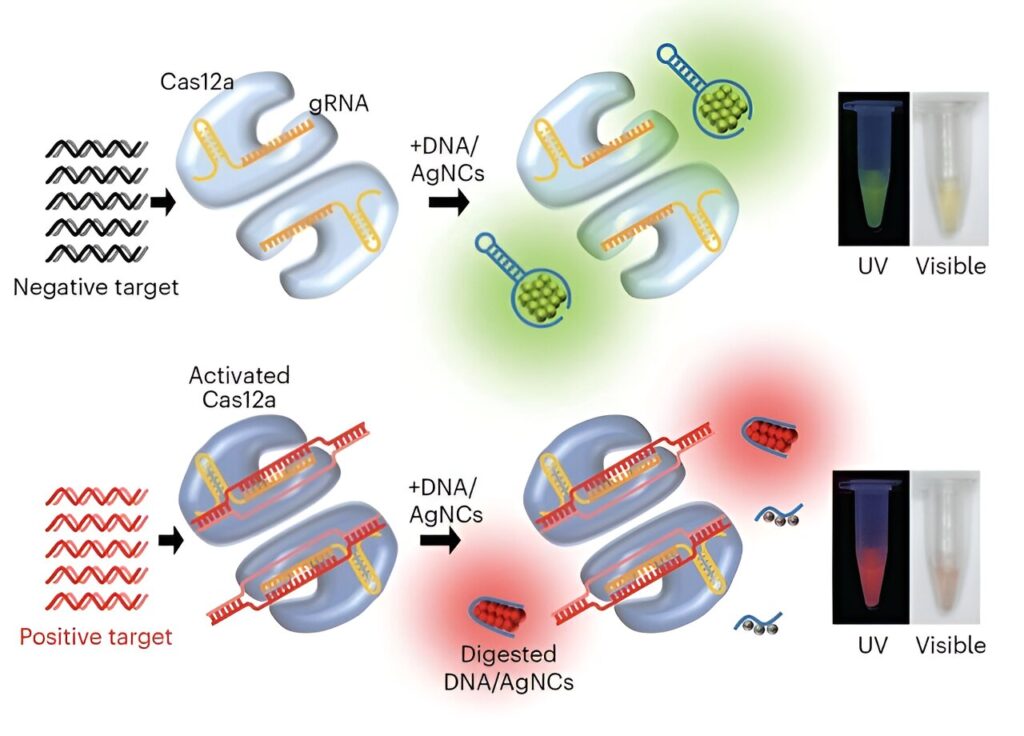
A study published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology shows that this low-cost tool, called Subak, is effective at telling when nuclease digestion has occurred, which is when an enzyme called nuclease breaks down nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA, into smaller fragments.
The traditional way of identifying nuclease activity, Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) probe, costs 62 times more to produce than the Subak reporter.
“Subak reporter is more cost-effective and simpler than FRET-based systems, offering an alternative method for detecting nuclease activity,” said Kim, the Robert C. Womack Chair in the Lyle School of Engineering at SMU and principal investigator of the BAST Lab. “Many nucleic acid detection methods today, such as PCR and DETECTR, still rely on the use of FRET probes in their final steps.”
Unlike PCR, DETECTR (DNA endonuclease-targeted CRISPR trans reporter) is an easier assay, or test, that relies on CRISPR-Cas nuclease for pathogenic DNA detection. Kim and the researchers at UT Austin have successfully replaced the FRET probe with Subak reporter in the DETECTR assay, thus substantially reducing the assay cost.
Subak reporters are based on a special class of what are known as fluorescent silver nanoclusters. They are made up of 13 silver atoms wrapped around a short DNA strand—an organic/inorganic composite nanomaterial that is too small to be visible to the naked eye and ranging in size from 1 to 3 nanometers (one billionth of a meter) in size.
Nanomaterials at this length scale can be highly luminescent, such as quantum dots, and exhibit different colors. Fluorescent nanomaterials have found applications in TV displays and in biosensing, such as the Subak reporter.
Lead researcher Tim Yeh, an Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering at the Cockrell School of Engineering at UT Austin, and his team programmed the Subak reporters to emit a different color when they are digested by nucleases.
“These DNA-templated silver nanoclusters initially emit green fluorescence, but undergo a remarkable color-switching to bright red when DNA is fragmented by nucleases,” Kim said. “The color change of Subak reporters is easily visible under a UV lamp,” even though the actual device is miniscule.
Subak reporters cost just $1 per nanomolecule to make. In contrast, FRET—which requires using different fluorescent dyes that require more to get results—costs $62 per nanomolecule to produce, Kim said.
Kim and Madhav L. Ghimire, SMU’s Dean’s Postdoctoral Fellow in SMU’s Moody School of Graduate and Advanced Studies, worked with Yeh to optimize and characterize the DNA/AgNC silver nanoclusters. This included increasing the intensity of the green and red fluorescence before and after fragmentation by nucleases.
Characterization involved confirming the size, structure and the stability of the nanoclusters in specific environments.
“Optimization of these low-cost detectors is essential to monitor their fluorescence properties, ensuring nanocluster’s stability, controlling size and structure, and most importantly to enhance their sensitivity and selectivity in various environmental conditions, making them more reliable for the sensing purpose,” Ghimire said.
In addition to further testing of the Subak reporter for nuclease digestion, the team also wants to investigate if it can be a probe for other biological targets.