The need for sustainable and environment-friendly solutions has accelerated the global demand for green and renewable technologies. In this regard, semiconductor photocatalysts have emerged as an attractive solution, owing to their potential in mitigating pollutants and harnessing solar energy efficiently. Photocatalysts are materials that initiate chemical reactions when exposed to light.
Despite their progress, commonly used photocatalysts suffer from reduced photocatalytic activity and a narrow operation range within the visible light spectrum. Additionally, they are difficult to recover from water-based solutions, limiting their applications in continuous processes.
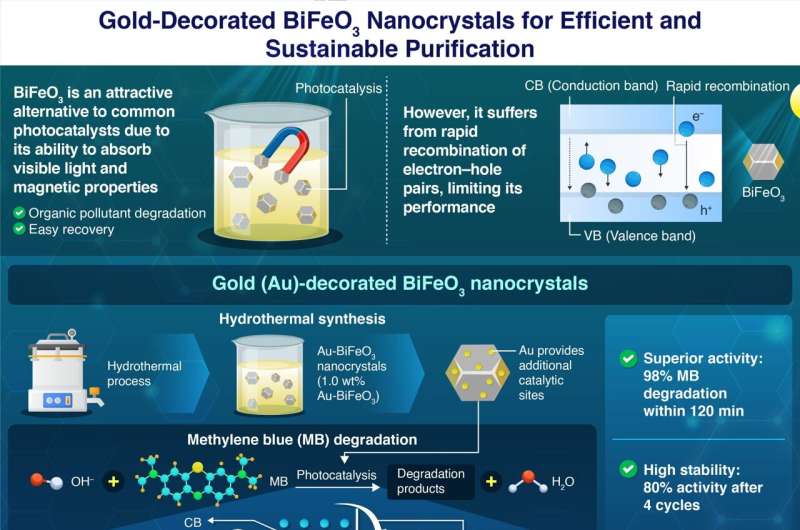
Bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3), with its narrow band gap and magnetic properties, is an attractive alternative photocatalyst. The narrow band gap of BiFeO3 allows efficient utilization of light in the visible region to excite electrons from the valence band to the conduction band, leaving behind vacant holes. The excited electrons and holes both could induce chemical reactions that lead to the degradation of pollutants in an aqueous solution.
In addition, the ferromagnetic property enables easy recovery of BiFeO3 from the solution. However, similar to common photocatalysts, BiFeO3 also suffers from rapid recombination of electron–hole pairs, significantly limiting its photocatalytic activity.
To address this issue, a team of researchers led by Associate Professor Tso-Fu Mark Chang from the Institute of Innovative Research at the Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan, developed novel gold (Au) nanoparticle-decorated BiFeO3 nanocrystals. Their study was published online in the journal ACS Applied Nano Materials on April 5.
Dr. Chang explains, “The incorporation of Au nanostructures in BiFeO3 can introduce more active sites for photodegradation reactions, owing to Au nanoparticle’s unique localized surface plasmon resonance, and the transfer of the excited electrons in the BiFeO3 to the gold domain suppresses the recombination of electron–hole pairs. The newly developed Au-decorated BiFeO3 nanocrystals leverage the synergistic characteristics of both mechanisms.”
The researchers fabricated the Au-BiFeO3 nanocrystals through a hydrothermal synthesis method and a simple solution process to decorate BiFeO3 with different amounts of Au. The team optimized the photocatalytic activity of the Au-BiFeO3 nanocrystals by evaluating their efficacy in degrading methylene blue (MB), a common denim dye. MB is highly soluble in water, posing a significant risk to aquatic life and human health. This also makes it the ideal pollutant to test the efficacy of photocatalysts.
Experiments revealed that the sample with 1.0% Au by weight exhibited the best activity, achieving an impressive 98% degradation efficiency under a 500-Watt xenon lamp within 120 minutes. Moreover, it also retained 80% of its original activity after four 120-minute cycles, demonstrating excellent stability. Additionally, there was negligible effect of Au on the magnetic properties of BiFeO3, suggesting excellent recyclability.
The researchers also studied the mechanisms by which Au enhances photocatalytic activity. When an Au-BiFeO3 nanocrystal is illuminated by light at suitable wavelengths, electrons in BiFeO3 are excited to the conduction band.
Unlike the recombination that occurs in bare BiFeO3, the introduction of Au, which has a less negative fermi level than the conduction band of BiFeO3, facilitates the transfer of excited electrons from the conduction band to the Au domain, thereby promoting the accumulation of holes in BiFeO3. This enhances the photocatalytic activity of BiFeO3, enabling it to more easily induce the generation of hydroxy radicals in aqueous solutions. These hydroxyl radicals are highly active and readily attack MB molecules in the aqueous solution, thus converting them to harmless products.
“These findings enhance our understanding of gold−semiconductor interactions in photocatalysis and pave the way for the design and development of advanced nanocrystal materials,” remarks Dr. Chang. “Overall, our study highlights the promising activity and recyclability of Au-BiFeO3, underscoring its potential in efficient and sustainable environmental pollutant degradation.”

