Blue energy has the potential to provide a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. In simple terms, it involves harnessing the energy produced when the ions in a salt solution move from high to low concentrations.
A team including researchers from Osaka University has probed the effect of voltage on the passage of ions through a nanopore membrane to demonstrate greater control of the process.
In a study recently published in ACS Nano the researchers looked at tailoring the flow of ions through the array of nanopores that make up their membrane, and how this control could make applying the technology on a large scale a reality.
If the membranes are made from a charged material, nanopores can cause a current to flow through them by attracting solution ions with the opposite charge. The ions with the same charge can then move through the pore generating the current. This means that the pore material is very important and choosing it has been the means of controlling the flow and current to date.
However, producing the exact same pore structures in a range of different materials to understand their comparative performances is challenging. The researchers therefore decided to investigate another way of tailoring the flow of ions across nanopore membranes.
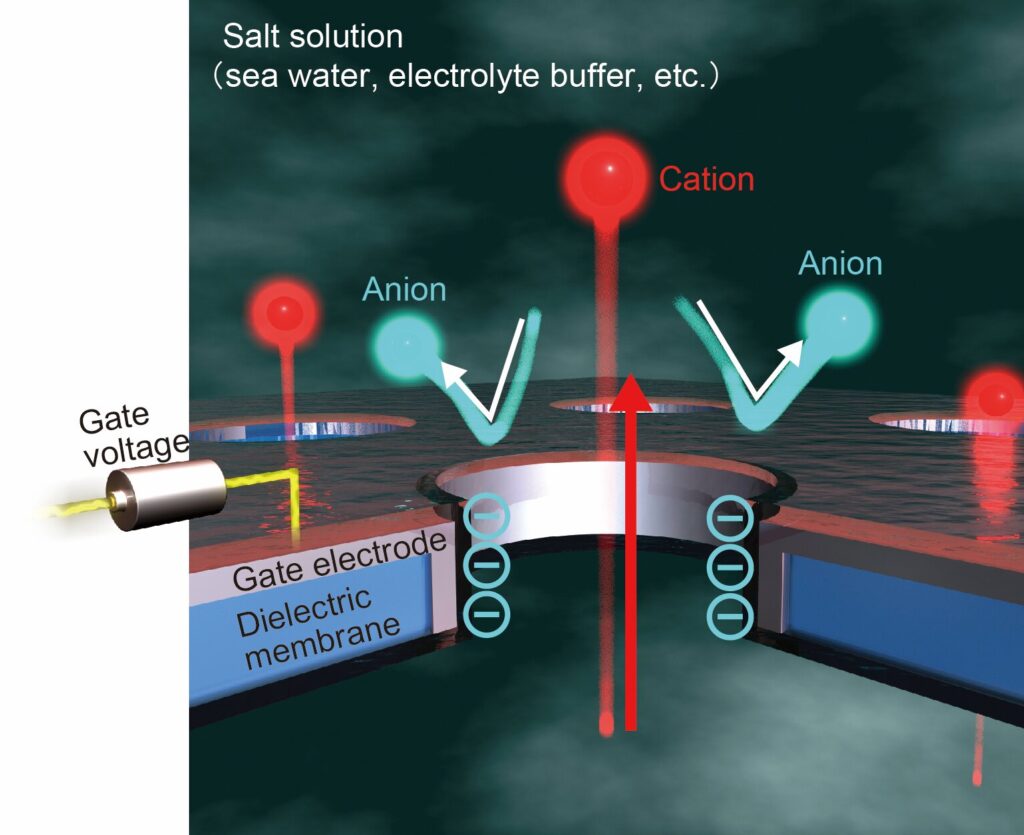
“Instead of simply using the basic surface charge of our membrane to dictate the flow, we looked at what happens when voltages are applied,” explains study lead author Makusu Tsutsui. “We used a gate electrode embedded across the membrane to control the field through voltage in a similar way to how semiconductor transistors work in conventional circuits.”
The researchers found that with no voltage applied there was no charge generated by the flow of cations—positively charged ions—because they were attracted to the negatively charged membrane surface.
However, if different voltages were applied, this performance could be tuned to allow cations to flow, even providing complete selectivity for cations. This led to a six-fold increase in the osmotic energy efficiency.
“By enhancing the charge density at the surface of the nanopores that make up the membrane, we achieved a power density of 15 W/m2,” says senior author Tomoji Kawai. “This is very encouraging in terms of progressing the technology.”
The study findings reveal the potential for scaling nanopore membranes for everyday application. It is hoped that nanopore osmotic power generators will provide a means of bringing blue energy to the mainstream for a more sustainable energy future.