by KeAi Communications Co.
The electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide into high-value chemicals and fuels offers a promising strategy for addressing the global energy crisis and worsening environmental issues. However, the high thermodynamic stability of CO2 molecules, competitive hydrogen evolution reactions, and the complexity of products pose significant challenges. Therefore, the selection and design of electrocatalysts are crucial for improving product selectivity and energy efficiency.
In a study published in the journal ChemPhysMater, a team of researchers from China has introduced a novel approach: the rapid joule-heating synthesis method that ensures the uniform dispersion of metal nanoparticles (NPs) on carbon supports and enhances the electron conductivity of catalysts.
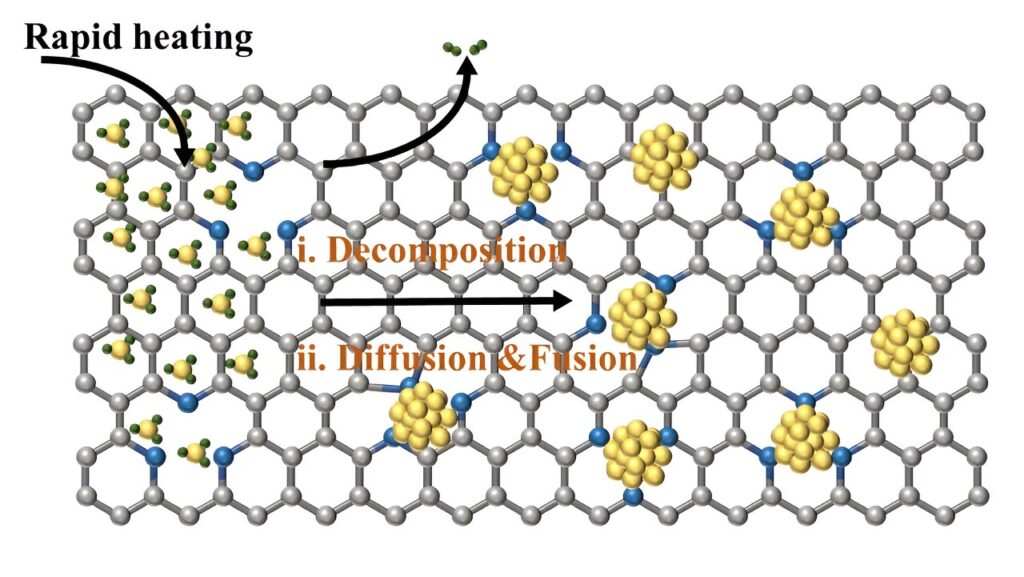
The functional nanoparticles dispersed on conductive carbon offer substantial benefits to improve the efficiency and selectivity of CO2 reduction. The carbon supports facilitate efficient electron and heat transfer, while also dispersing and stabilizing NPs to prevent aggregation. However, during carbonization synthesis, metal nanoparticles often aggregate to reduce their surface energy, leading to a loss of active area and catalytic deactivation.
Through rapid thermal shock treatment, the researchers achieved a uniform dispersion of metal nanoparticles on a carbon substrate (M-PANI-T). The short duration of thermal shock inhibited the migration of metal atoms, and defects in carbon generated by pyrolysis played a crucial role in anchoring metal nanoparticles. By adjusting the treatment time to varying temperatures, the researchers explored the impact on catalytic performance. Electrochemical testing revealed that catalyst performance depends on both the metal active sites and the carbon supports, rather than solely on individual factors.
According to Jintao Zhang, senior investigator of the study, this breakthrough in the field of functional nanoparticles prepared on carbon substrates demonstrates that the joule-heating shock method has good universality and excellent electrocatalytic activity. This method can be used to prepare various catalysts for carbon-supported metal nanoparticles, significantly reducing time and raw material costs while providing valuable theoretical insights for future catalyst design.
Provided by
KeAi Communications Co.