Hematite (α-Fe2O3) is considered one of the most promising materials for photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting under solar light. However, the drawbacks of lower charge transfer efficiency and slow oxygen evolution reaction (OER) kinetics limit the practical application of α-Fe2O3 photoanodes. Therefore, efforts have been made to promote the PEC properties of α-Fe2O3, such as elemental doping, morphology modulation, and construction of heterojunctions.
In a study published in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, the research group led by Prof. Lu Canzhong from the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported a novel α-Fe2O3 photoanode with multilayered In2O3/Co-Mn nanostructure for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting.
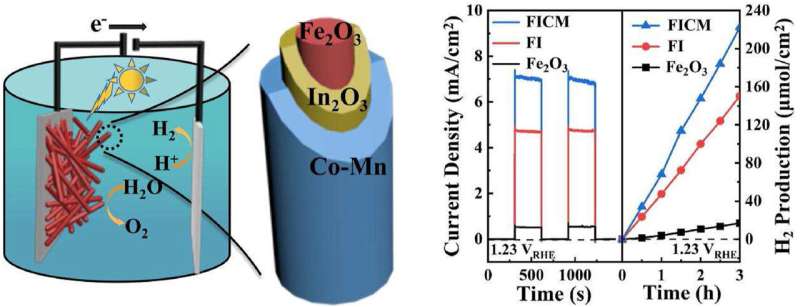
The researchers synthesized α-Fe2O3 nanorod arrays using classic hydrothermal methods, followed by a layer of In2O3 nanolayers covered on the α-Fe2O3 using wet chemical deposition, and ultimately covered with a layer of nanosheet combining ultrathin non-crystalline Co(OH)x and Mn3O4 nanocrystals (Co-Mn nanosheet coating) using electrodeposition.
By linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) testing, the researchers found that the high photocurrent density of In2O3/Co-Mn modified α-Fe2O3 photoanode is 13.8 times that of ordinary α-Fe2O3 materials. They also tested the efficiency of incident photons photocurrent(IPCE), and found that the IPCE value of pristine α-Fe2O3 at an incident light wavelength of 400 nm is only 9.5 %, and the IPCE value of In2O3/Co-Mn modified α-Fe2O3 photoanode is 57.9 %.
In addition, they evaluated the H2 production rate. The In2O3/Co-Mn modified α-Fe2O3 photoanode production reached 74.10 mmol/cm2/h, which was 13.12 times higher than the α-Fe2O3 photoanode.
The researchers also revealed that the loading of In2O3 nanolayers significantly improves the photoelectrochemical water oxidation activity of α-Fe2O3 nanorods. The heterojunction formed by the In2O3 passivation layer and α-Fe2O3 effectively promotes charge separation, increasing photocurrent density.
The Co-Mn nanosheet coating loading helps improve the water oxidation performance of α-Fe2O3, and this multi-layer structure enables efficient photoelectrochemical water decomposition of α-Fe2O3 nanorods.