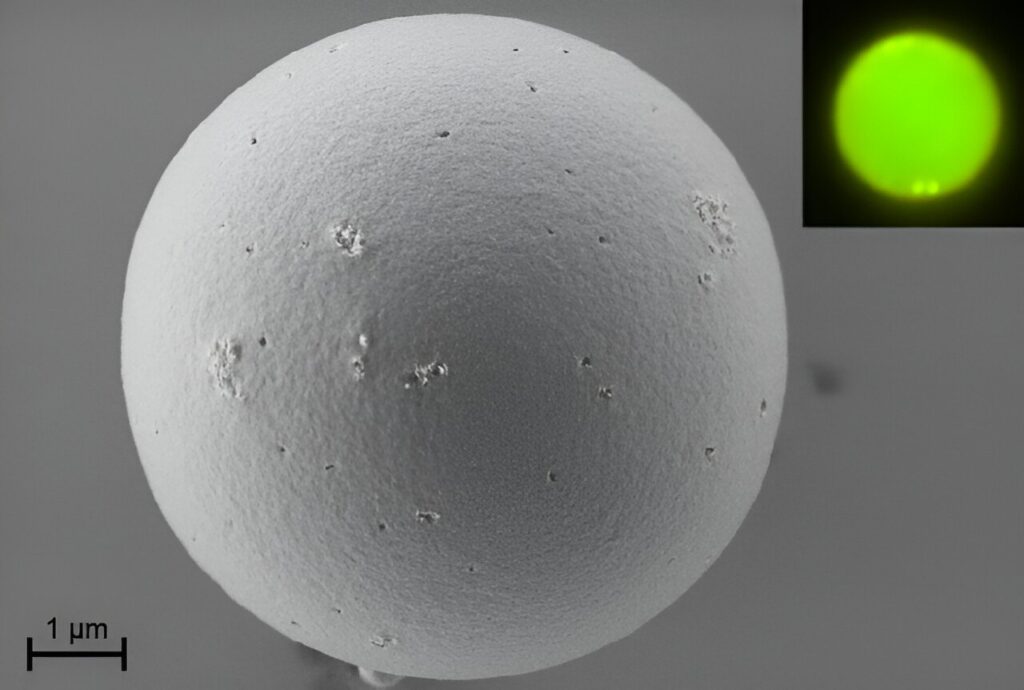
Researchers at IMDEA Nanociencia have fabricated high quality microspheres from conjugated organic polymer blends with excellent lasing properties. The laser emission of the microspheres has the highest quality factor reported to date, Q>18,000.
Dielectric optical microresonators confine and concentrate light in a tiny circular path due to multiple near total internal reflections at the curved dielectric-air interface, where light interferes constructively for certain wavelengths. These microresonators offer the possibility to achieve control of light confinement and propagation through precise adjustment of their shape, size and refractive index.
Among them, spherical resonators are particularly interesting due to their high Q factors (ratio of the resonance frequency over its bandwidth) of the corresponding Mie resonances, or “whispering gallery modes.”
The Q factor is in essence a measure of how well light can be trapped in the microsphere over time and high Q factors correspond to narrow lasing linewidths, a desired feature when designing laser applications.
The narrow resonances enable applications in the optical sensing field, including devices with high sensitivity to small physical or chemical variations in the optical near field of the resonators. Also, high Q factors pave the way for applications in the field of amplified spontaneous emission and lasing of microspheres made with luminescent materials.
So far, microlasers based on conjugated polymers have been reported with typical Q factors around 1,000. Conjugated polymers have emerged as excellent organic laser materials for their outstanding optoelectrical properties and facile processability.
Among all resonator geometries, microspheres made of conjugated polymers combine large optical absorption with high photoluminescence quantum yield, affording an increase of brightness with respect to commercial dye-doped microspheres under the same photoexcitation conditions.
Researchers at IMDEA Nanociencia institute (Madrid, Spain), led by Dr. Reinhold Wannemacher and Dr. Juan Cabanillas, have now reported microspheres based on conjugated polymer blends exhibiting lasing with the highest quality factor reported to date, Q> 18,000.
The reported low lasing thresholds are based on the energy transfer (Förster Resonant Energy Transfer, FRET) between the polymer constituents of the blends, a mechanism that reduces residual absorption at the lasing wavelength. Such low thresholds are promising for the development of microlasers which can be pumped by low-cost laser diodes.
The results have been published in Advanced Optical Materials.
Together, low thresholds and narrow lasing linewidths enable ultrasensitive detection of variations of physical parameters (pH, temperature) as well as chemical composition of the environment of the microspheres and, in the case of microspheres with surfaces functionalized by specific organic groups, ultra-sensitive and highly specific detection of biomolecules.
The latter is highly relevant for the development of portable and low cost biodetectors, which would enable rapid diagnosis of diseases at points of care.