Biomolecules-based materials hold great promise for malignant tumor phototherapy. However, current supramolecular biomaterials primarily suffer from poor tissue penetration, inadequate tumor accumulation, and particularly neglecting the unique benefits of chirality, thus significantly limiting their phototherapeutic efficacy.
Previously, designing near-infrared, circularly polarized, light-responsive supramolecular biomaterials with superior NIR chiroptical properties and enhanced phototherapeutic performance has remained a challenge.
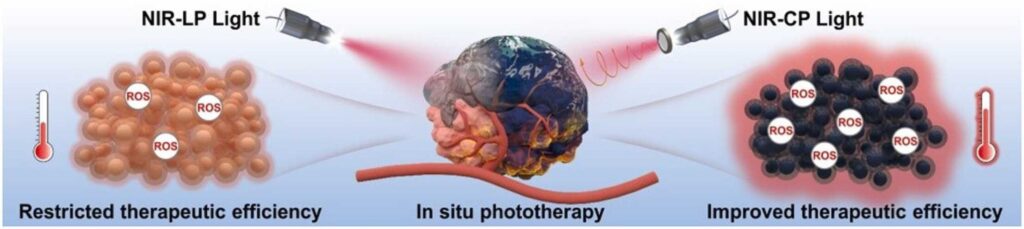
In a study published in Nano Today, a research group led by Prof. Chen Xueyuan from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter (FJIRSM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a novel NIR-CP light-responsive hybrid CuInSe2@ZnS quantum dots (CISe@ZnS QDs) hydrogel (QDs@L/D-Gel) for achieving distinctly enhanced therapeutic efficacy in vitro and in vivo upon exposure to 808-nm CP light.
Researchers fabricated the QDs@L/D-Gel by utilizing the self-assembly between CISe@ZnS QDs and amino acid precursors. The obtained QDs@L/D-Gel showcased distinctive NIR chiroptical activity (|gabs| up to 1.3 × 10-2 and |glum| up to 3.4 × 10-3), a prominently improved photothermal conversion efficiency (PCE) of 43%, and elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production upon exposure to 808-nm CP light.
Benefiting from NIR-CP light improved phototherapeutic efficacy, highly enhanced tumor retention (> 72 h), and superior biocompatibility, researchers observed a remarkably enhanced phototherapeutic efficacy (tumor inhibition rate = 83%) for QDs@L-Gel treated mice after NIR-CP light treatment without causing any toxic side effects, outperforming the identical material exposed to linearly polarized (LP) light directly emitted from an 808-nm laser device.
Additionally, researchers conducted circular dichroism (CD) spectra to investigate the supramolecular conformation of the obtained hybrid QD hydrogels. The mirror symmetry CD curves of L-Gel and D-Gel revealed that the L-Gel and D-Gel were self-assembled from opposite chiral units, respectively.
This study provides an innovative view on the utilization of NIR-CP light for achieving more rational and effective phototherapy, thereby accelerating the clinical translation of biomolecules-based materials for versatile biomedical applications.