Schizophrenia is a complicated mental health disorder accompanied by a wide range of symptoms such as hallucinations, impaired cognitive ability, and disorganized speech or behavior. It has been associated with anomalies in neurotransmission due to the imbalance of chemical neurotransmitters.
Current treatment strategies against schizophrenia involve the administration of antipsychotic drugs, which can cause adverse effects and are associated with a high risk of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, in patients, response to therapeutic drugs is often inadequate as the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a protective barrier of cells, strictly regulates the movement of ions and molecules into the brain.
To overcome the hurdle of BBB and facilitate the transport of therapeutic drugs into brain tissue to treat schizophrenia, researchers have explored the applicability of receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) using low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1).
This research was conducted by a team led by Associate Professor Eijiro Miyako from Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST), including Prof. Yukio Ago from Hiroshima University, Prof. Shinsaku Nakagawa from Osaka University, Prof. Takatsugu Hirokawa from Tsukuba University, and Dr. Kotaro Sakamoto, Senior Principal Scientist at Ichimaru Pharcos Co., Ltd. Their study was published in the JACS Au journal.
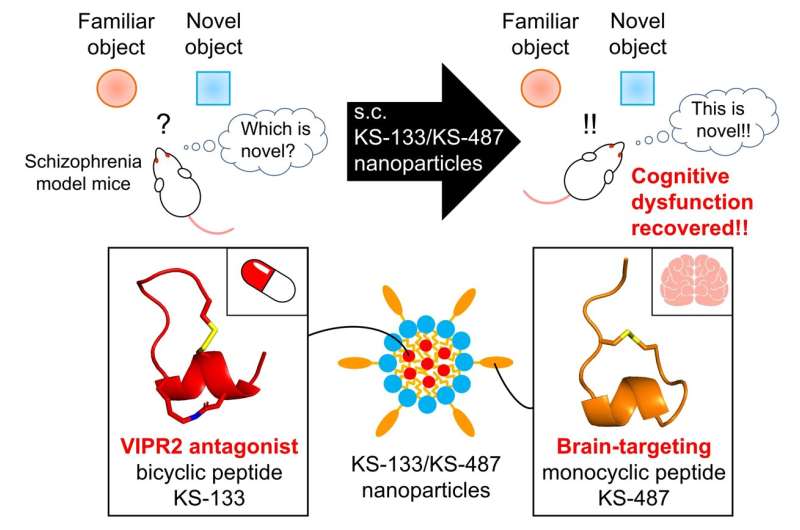
The researchers were inspired by previous findings showing the interactions of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 2 (VIPR2) gene duplication in schizophrenia and their own discovery of a novel peptide, KS-133. The novel peptide, KS-133, has selective antagonist activity with VIPR2, leading to its downregulation. However, the major limitation associated with KS-133 was its poor permeability across BBB.
To facilitate the effective transport of KS-133 into the brain, they developed a brain-targeting peptide, KS-487, that could specifically bind to LRP1 and influence RMT. Finally, the researchers developed a novel nanoparticle-based drug delivery system (DDS) where KS-133 peptide was encapsulated with KS-487 targeting peptide and studied its efficacy in treating schizophrenia.
The administration of peptide formulations via the DDS resulted in the effective distribution of the drug in the brains of mice. Drug release profiles assessed by pharmacokinetic analysis confirmed the role of the brain-targeting peptide in transporting KS-133 into the brain. Furthermore, the efficacy of DDS was evaluated in mice with induced schizophrenia by elevated activation of VIPR2. Mice treated with KS-133/KS-487 nanoparticles showed significant improvement in cognitive functions during novel object recognition tests, which could be attributed to the inhibition of VIPR2.
Explaining the real-life applications and potential of their study, Dr. Miyako states, “Existing drugs only have mechanisms involving neurotransmitter modulation, and their therapeutic effects are limited, especially for cognitive dysfunction. Thus, our peptide formulation could be used as a novel drug to restore cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia.”
In summary, this study by Dr. Miyako and co-researchers provides preclinical evidence of a novel therapeutic strategy for targeting VIPR2 that could improve cognitive impairment in schizophrenia.
“Going ahead, we will extend our study to involve cells and animal models, as well as human clinical trials, to confirm the efficacy and safety of this peptide formulation and promote its development as a new treatment for schizophrenia within 5 years,” concludes Dr. Miyako, optimistic about the long-term implications of their study.
The researchers are hopeful that the discovery and development of novel DDS utilizing bio-compatible peptides revolutionizes the treatment landscape of schizophrenia.

