Since prehistoric times, humans have used fire to transform raw materials into valuable goods. Examples include using flames to turn clay into pottery, and silica into glass.
The practice continues today with industry employing a highly sophisticated version of the technique—flame aerosol synthesis—to create nanoparticles that serve as key ingredients in everything from inks to air filters.
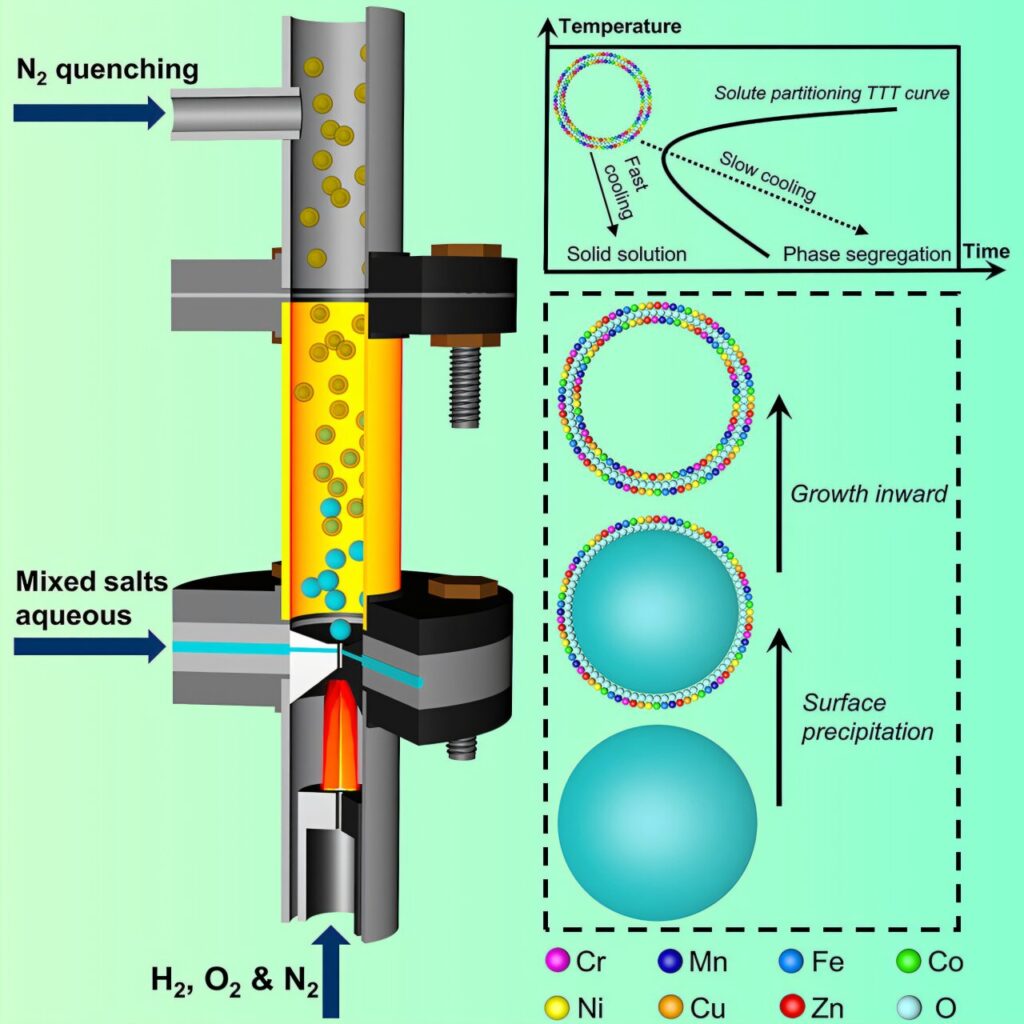
While effective, flame aerosol synthesis is not without limitations, including challenges with manipulating the flame, achieving precise control over the size and distribution of nanoparticles, and cost.
Two new research studies co-led by University at Buffalo engineers address these shortcomings. The studies center on a unique flame aerosol system that the engineers created which, they say, is versatile, easy-to-use and cost effective.
The most recent study, published Oct. 30 in Nature Communications, describes how the research team used the system to create metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), which are porous nanomaterials used in a variety of fields including energy, the environment, and health and medicine.
“This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first time that flame aerosol technology has been applied to create MOFs,” says one of the study’s lead authors, Mark Swihart, Ph.D., SUNY Distinguished Professor and chair of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering in the UB School of Engineering and Applied Sciences.
Most MOFs are created via a liquid chemical reaction. While effective, especially in producing materials with a high degree of crystallinity, the method can be time-consuming and expensive.
By contrast, the flame aerosol system has the potential to be much quicker—and less expensive—because it requires only one step. While the MOFs it produces have lower porosity than conventional MOFs, their unique properties—including small grain size, short-range ordered structures, and high thermal stability—could lead to new materials and commercial uses, researchers say.
Lastly, the flame aerosol system circumvents thermodynamic barriers. This allows the mixing of any two metal elements into a single MOF with properties that are ideal for catalysis, sensing, energy storage and other fields, researchers say.
The earlier study, published Aug. 27 in Matter, reports on the flame aerosol system’s potential for creating high-entropy ceramic nanomaterials. These highly stable nanomaterials are made of multiple elements—usually five or more in near equal proportions. They have unique properties that, like MOFs, make them ideal for energy storage, catalysis, sensing and other applications.
In experiments using the flame aerosol system, the research team demonstrated the flexibility of the method by creating nanoparticles incorporating up to 22 elements. As an application, they demonstrated a carbon dioxide reduction catalyst that exhibited impressive strength and durability, exceeding that of conventional catalysts.
“The flame reactor is a scalable, one-step and incredibly versatile way to fabricate high-entropy nanoceramics, as well as other materials,” says Swihart, also a SUNY Empire Innovation Professor and faculty member in UB’s RENEW Institute.