Cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases to treat due to its complexity and tendency to metastasize (spread into, or invade, nearby tissues or distant places in the body to form new tumors). Traditional therapies, such as chemotherapy and radiation, often face limitations like non-specific targeting and severe side effects.
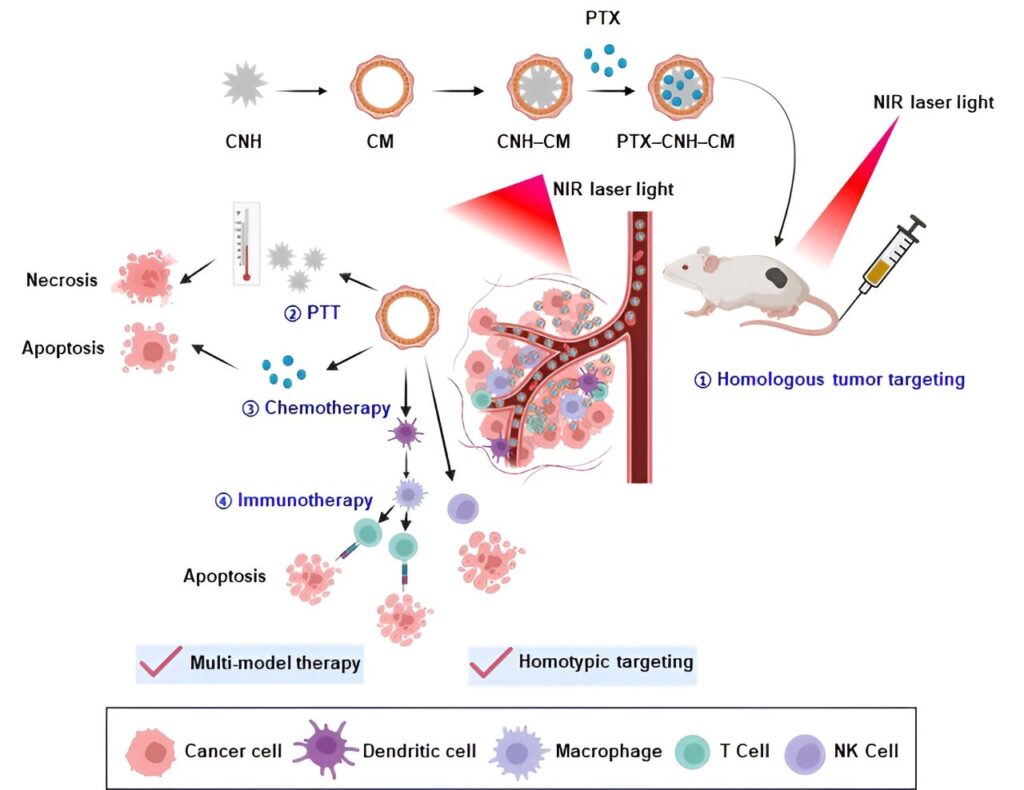
In response, researchers are turning to innovative approaches that combine multiple therapeutic modalities to address these issues. This study explores a cutting-edge solution involving CNHs to create a multimodal cancer phototheranostic platform integrating photothermal therapy (PTT), immunotherapy, and chemotherapy.
PTT utilizes light-sensitive materials that can induce photothermal effect [conversion of near-infrared (NIR) light to heat] and activate immune responses to destroy cancer cells. While PTT is effective in targeting solid tumors, it has significant limitations.
One major drawback is its inability to eliminate cancer cells outside the irradiation region, making it less effective against metastatic diseases. Additionally, PTT’s efficacy is limited by the depth of NIR light penetration, which can hinder its ability to treat deep-seated tumors.
To address these limitations, a team of researchers led by Associate Professor Eijiro Miyako from the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST), have now developed cancer cell membrane (CM)-wrapped CNH nanoparticles for the delivery of paclitaxel (PTX) for the treatment of colon cancer.
These nanoparticles leverage the unique properties of CNHs and the targeting capabilities of cancer cell membranes. By using cancer membranes, the nanoparticles can specifically target cancer cells, thereby enhancing the precision of PTT.
Their research findings were published in Small Science.
To further improve therapeutic outcomes, researchers encapsulated the chemotherapeutic or anticancer drug PTX within the CNH‒CM complexes. These nanoparticles were designed not only to deliver therapeutic agents directly to tumors, but also to maximize the efficacy of the drug. They tested these nanoparticles for tumor targeting, drug delivery, and therapeutic effects in experimental models.
The researchers discovered that the PTX-CNH‒CM complexes exhibited high accumulation and prolonged retention at the tumor site. This resulted in a stronger chemotherapeutic effect compared to free PTX. Additionally, the nanoparticles demonstrated a robust photothermal effect and significant immune responses, effectively destroying tumors.
“The high surface area and unique properties of CNH enhances drug loading and photothermal conversion efficiency. In addition, CM enables targeted delivery, while the encapsulated PTX and immunotherapeutic properties of the carrier provide additional therapeutic benefits. Thus, the integration of PTT, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy within a single platform resulted in synergistic effects, overcoming the limitations of standalone PTT,” explains Dr. Miyako.
The biomimetic CNH nanocomplexes demonstrated excellent tumor-targeting, controlled drug-releasing behavior, and cancer cell death induction, leading to a strong antitumor response. These findings suggest that the biomimetic CNH complex system represents a promising avenue for developing more precise and effective cancer treatments, marking a significant advancement in cancer therapy.
“Our study provides an effective and precise approach for the treatment of cancer and metastatic diseases by combining the advantages of multiple therapeutic modalities into a single platform. We anticipate that this technology will be available for clinical trials in 10 years,” concludes Dr. Miyako.