
The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) has developed a hybrid nano-microscope capable of simultaneously measuring various nano-material properties. This nano-microscope is essential for researching the properties of nano-composite materials and is also suitable for commercialization. It is expected to promote the development of industries for related materials and equipment.
The newly developed microscope is a hybrid nano-microscope combining the functions of atomic force microscopy, photo-induced force microscopy, and electrostatic force microscopy. Instead of using lenses, it employs a fine functional probe to tap the sample, allowing simultaneous measurement of the optical and electrical properties as well as the shape of nano-materials with a single scan.
The bilayer graphene is one of the typical nano-materials that benefit from using the hybrid nano-microscope. It has great potential for applications because of its superior mechanical strength, flexibility, and high thermal conductivity compared to monolayer graphene. The bilayer graphene exhibits various properties, including superconductivity, depending on the voltage applied to each layer or the twisted angle between two layers.
The KRISS Material Property Metrology Group has elucidated the principles of the unique infrared absorption response observed in bilayer graphene with the hybrid nano-microscope. The KRISS researchers confirmed that this phenomenon is caused by the charge imbalance between the two layers of graphene. They also experimentally demonstrated the ability to control infrared absorption by intentionally inducing and adjusting the charge imbalance.
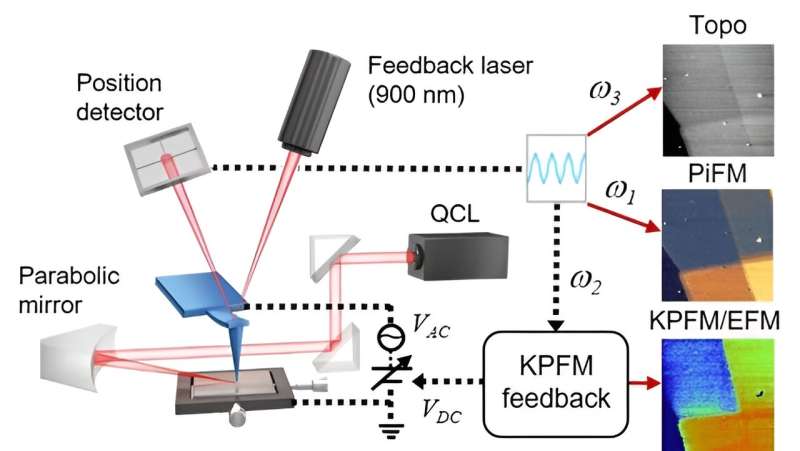
Conventional nano-microscopes could only measure a single property of a material at a time, making it challenging to measure and analyze composite properties. Although there were some cases of measuring two properties simultaneously, its commercialization was still restrictive because it was demanding to manufacture the equipment.
The novel nano-microscope developed by KRISS can be easily applied to industrial settings as it can be manufactured without significant changes to the structure of the existing atomic force microscope. The KRISS research team, therefore, is the first to develop a hybrid nano-microscope that can be commercialized.
By expanding its measurement properties to the magnetic properties besides the optical and electrical properties, it will be possible to observe all three properties simultaneously on the nano-scale. This is expected to accelerate research on the properties of various nano-composite materials, including quantum materials, contributing to the development of nano-materials, parts, and equipment.
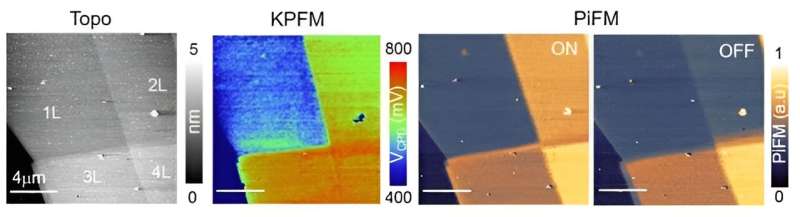
Another strength of this technology is the ability to induce localized changes in properties. By using the microscopic probe to scratch the sample surface and adjusting the amount of applied electrons, it is possible to simultaneously control the optical and electrical properties of the component like a switch. This can be useful for the design of circuits and sophisticated devices applying composite properties.
Dr. Eun Seong Lee, a principal researcher from the KRISS Material Property Metrology Group, said, “This achievement is the culmination of our research experience in nano-measurement since 2015. We hope to secure a leading position in the research on new materials by developing nano-measurement technology for composite properties.”
The research is published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.

