Blue lasers, lasers that emit a light beam with a wavelength between 400 nm and 500 nm, are key components of various technologies, ranging from high-resolution displays to printers, medical imaging tools and data storage solutions. A key advantage of these lasers is that they generate coherent and intense light beams that can be leveraged to develop highly advanced optical technologies.
One approach to developing blue lasers entails the use of colloidal quantum dots (CQDs). These are nanoscale semiconducting particles with unique optical properties associated with their size.
Lasers based on these nanoscale particles could have notable advantages, including enhanced power-efficiency and tunability. Most quantum dot-based lasers developed so far utilized cadmium (Cd) particles that emit red light, while efforts to introduce similar blue light-emitting lasers were sparser.
Researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently realized a new blue laser technology that leverages CQDs. Their proposed laser design, outlined in a paper in Nature Nanotechnology, is based on quantum dots that combine zinc selenide (ZnSe) and zinc sulfide (ZnS) in a core-shell structure.
“CQDs are solution-grown materials with strong, tunable emission covering the whole visible spectrum, but the development of QD lasers has largely relied on Cd-containing red-emitting QDs, with technologically viable blue QD lasers remaining out of reach,” wrote Xuyang Lin, Yang Yang and their colleagues in their paper.
“We report on the realization of tunable and robust lasing using low-toxicity blue-emitting ZnSe–ZnS core–shell QDs that are compact in size yet still feature suppressed Auger recombination and long optical gain lifetime approaching 1 ns.”

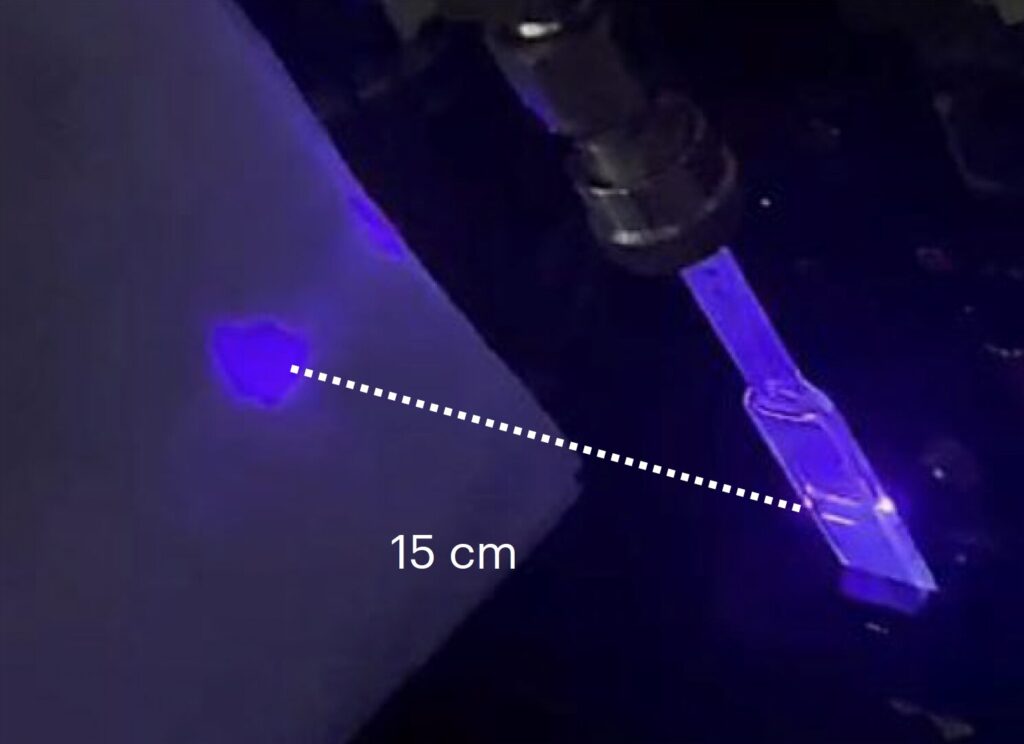
The ZnSe–ZnS quantum dots used by this team of researchers are highly compact and have a long optical gain lifetime. The researchers leveraged these quantum dots’ advantageous properties, using them as laser dyes, which are compounds typically dissolved in liquid solvents to produce dyes that amplify the light emitted by lasers.
Using this method, Lin, Yang and their colleagues realized the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) of blue light from the quantum dots. A further advantage of their CQD-based laser is that it exhibits low toxicity compared to previously introduced lasers utilizing Cd and cadmium selenide (CdSe) quantum dots.
“The blue QD laser is operated under quasi-continuous-wave excitation by solid-state nanosecond lasers,” wrote Lin, Yang and their colleagues.
“A Littrow-configuration cavity enables narrow linewidth (<0.2 nm), wavelength-tunable, coherent and stable laser outputs without circulating the solution. These results indicate the promise of ZnSe–ZnS QDs to fill the ‘blue gap’ of QD lasers and to replace less stable blue laser dyes for a multitude of applications.”
Overall, the results of this recent study highlight the potential of quantum dots based on ZnSe and ZnS for developing blue light-emitting laser technologies with low toxicity. In the future, the methods used by Lin, Yang and their colleagues could serve as an inspiration for other teams that are developing laser nanotechnologies, potentially also paving the way for the development of liquid CQDs-based lasers that emit ultraviolet (UV) light.