Cancer has a high death rate with delayed diagnosis of the disease being one of the main reasons for its fatality. Early diagnosis of cancer is vital to improving patient outcomes and in recent years, the development of diagnostic tools to detect early-stage cancer has gained a lot of attention.
Cancer cells utilize specific micro-ribonucleic acids (miRNAs)-small noncoding RNAs to regulate gene expression and promote tumor formation. While circulating miRNAs are viable biomarkers of early cancer disease, the identification of cancer-related miRNAs in blood and other body fluids remains a challenge.
In this light, a team of researchers led by Professor Takao Yasui from Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo), Japan, have focused their efforts on nanowire-based miRNA extraction and machine learning (ML) analysis to detect cancer-associated miRNAs in urine. Their research findings were published online in the journal Analytical Chemistry on October 18, 2024.
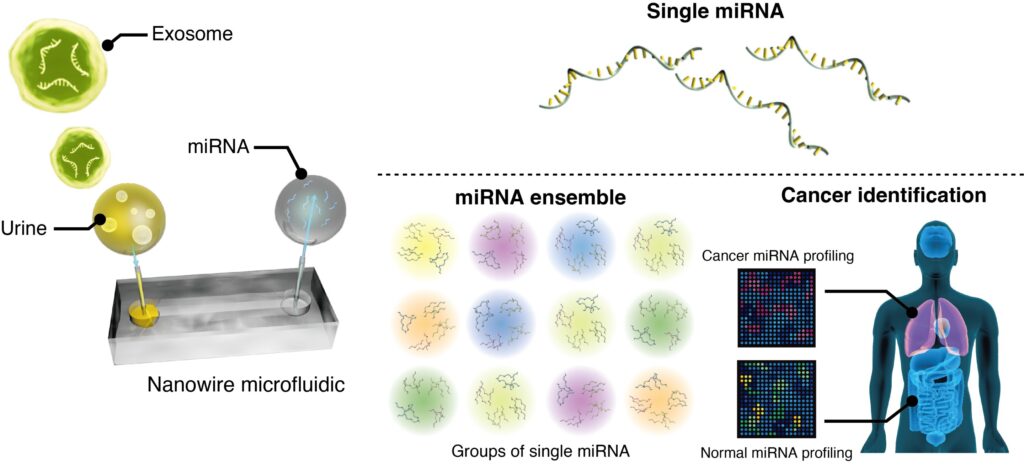
Elaborating on the rationale behind the present research, Yasui says, “Circulating miRNAs in the blood are mostly encapsulated in extracellular vesicles (EVs) and carry critical regulatory information. These miRNAs differ between healthy individuals and those with cancer. By utilizing zinc oxide (ZnO) nanowires to capture and extract miRNAs in urine, our research group has attempted to develop a non-invasive cancer detection tool.”
Initially, the scientists utilized ZnO nanowires to capture EVs in urine samples and incorporated microarray technology to identify specific gene sequences in EV-encapsulated miRNAs. The ultracentrifugation technique was further used to compare and validate the efficiency of miRNA capture by nanowires.
The results revealed that EVs containing miRNAs, including exosomes-unique subtypes of EVs with sizes ranging from 40 nm to 200 nm, were efficiently captured on nanowires. Moreover, the presence of 2,486 miRNA species was confirmed during the miRNA profiling analysis of 200 urine samples.

Driven by the discovery of more than 2,000 miRNA species in urine samples, Yasui and the team hypothesized that most of the miRNAs in blood could be transferred to urine during the filtration process in kidneys.
Subsequently, they employed a logistic regression classifier constructed using ML to identify lung cancer-associated urinary miRNA ensembles. The findings revealed one particular urinary miRNA ensemble, composed of 53 miRNA species, that could differentiate cancer and noncancer subjects with very high specificity and sensitivity.
Yasui states, “We also identified another urinary miRNA ensemble that could accurately detect stage-I lung cancer. Since urinary miRNA ensembles can predict early-stage lung cancer, we believe that urinary miRNA ensembles have sufficient potential to be developed as liquid biopsies for early-stage cancer prediction.”
Provided by
Institute of Science Tokyo