A review article published in the journal Antioxidants provides a detailed overview of nanoparticle-based strategies to improve the bioavailability and bioactivity of curcumin.
Study: Enhancing the Bioavailability and Bioactivity of Curcumin for Disease Prevention and Treatment. Image Credit: Microgen / Shutterstock
Background
Curcumin, turmeric’s main bioactive compound, is a polyphenol found in Curcuma longa roots. This compound has numerous health benefits, including anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-microbial, wound-healing, and lipid-lowering properties.
Curcumin has low bioavailability in human organs and is rapidly converted to a number of bioactive metabolites after intestinal absorption. Dried turmeric powder prepared from Curcuma longa roots contains about 2-5% of curcumin.
Curcumin consumed through dietary sources is sufficient to impact the gut microbiota. However, due to rapid metabolism, the concentration of intact curcumin in the circulation becomes very low (sub-micromolar concentrations), which is insufficient to trigger cellular signaling and gene expression, as observed in in vitro studies with cultured cells.
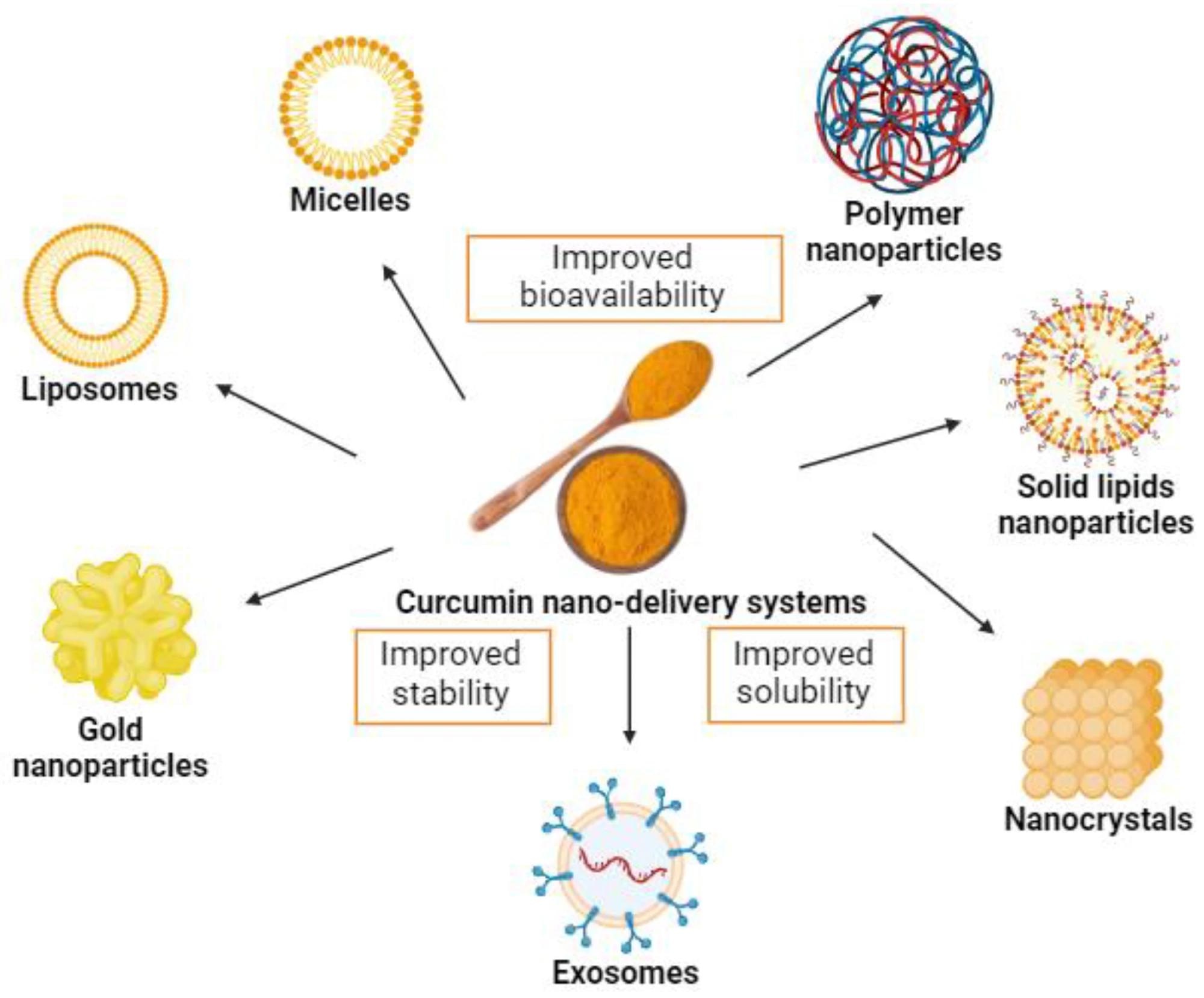 Examples of curcumin nano-delivery systems.
Examples of curcumin nano-delivery systems.
Strategies to increase curcumin bioavailability
Dietary curcumin is inefficiently absorbed across the intestinal epithelium and undergoes rapid metabolism and systemic elimination. In an aqueous solution with a neutral pH, the enol state of curcumin is formed, which reduces the stability of curcumin.
Several nanoformulations have been developed to increase curcumin concentration in the circulation as well as in specific cells, tissues, and organelles. These nanoformulations have been designed to increase curcumin solubility, improve stability during gastrointestinal absorption, alter absorption routes, and inhibit detoxification enzymes using adjuvants.
The latest generation of curcumin nanoformulations can increase free curcumin bioavailability in plasma by more than 100-fold and improve absorption, cellular uptake, permeability through the blood-brain barrier, and tissue distribution.
Factors that improve curcumin bioavailability include composition, size, and route of administration of nanoparticles. Curcumin preparations with smaller-size nanoparticles have been found to increase bioavailability when administered orally. In contrast, larger-size nanoparticles have been found to increase bioavailability when administered intravenously.
Curcumin nanoformulations can induce senescence in malignant and normal cells, thus effectively treating various cancer types and age-related diseases, including cardiometabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and liver, lung, and gastrointestinal diseases.
Regarding mode of action, existing evidence indicates that curcumin acts as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound to reduce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and modulate cellular signaling and gene expression related to inflammatory pathways. These activities work synergistically to maintain homeostasis of cellular macromolecules (proteins, DNA, and lipids).
These activities can be increased by incorporating curcumin in nanoparticle-based formulations, such as polymeric curcumin–bioperine–PLGA. The isomerization of curcumin to cis-trans curcumin is known to increase its ability to bind adenosine receptors. Incorporation of cis-trans curcumin into nanoformulations is considered to be a valuable strategy to increase its therapeutic efficacy against inflammatory diseases.
Regarding safety profile, recent clinical trials indicate that the majority of curcumin nanoformulations are well-tolerated and safe for use in humans.
Anti-microbial activities
Curcumin is known to exert an anti-microbial effect against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and this activity is beneficial for topical applications against skin infection and oral and intestinal applications. Moreover, curcumin can indirectly prevent infection by inhibiting bacterial growth in foods.
The anti-microbial activities of curcumin can be enhanced by incorporating it into nanoformulations. Administration of curcumin with other compounds, such as antibiotics, honey, or other polyphenols, can also increase its anti-microbial and biofilm inhibitory activities.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations in the gastrointestinal tract
Several nanotechnology-based systems, such as micelles, liposomes, exosomes, phospholipid complexes, nanoemulsions, nanostructured lipid carriers, and biopolymer nanoparticles, have been found to increase oral curcumin bioavailability.
Nanoparticle curcumin called ‘Theracurmin’ has been found to suppress colitis in mice by modulating gut microbiota. Improvement in gut microbiota composition has also been achieved using nanobubble curcumin extract. Curcumin loaded with nanostructured lipid carriers has been found to reduce colonic inflammation in animals.
The incorporation of curcumin in liposomes has been found to increase its anticancer activity by improving gastrointestinal absorption. Moreover, the administration of curcumin with other bioactive compounds, such as piperine and salsalate, has been found to increase curcumin bioavailability and bioactivity.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations in liver and adipose tissue
Curcumin nanoformulations with adjuvants, such as piperine and quercetin, have been found to increase its bioavailability and bioactivity significantly. Various nanotechnology-based delivery systems, such as micelles, liposomes, polymeric, metal, and solid lipid nanoparticles, have been found to increase curcumin bioavailability.
The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic properties of curcumin make it a potential therapeutic compound for liver diseases. In liver diseases, curcumin nanoformulations have been found to increase its therapeutic efficacy by increasing curcumin solubility, bioavailability, and membrane permeability and improving its pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and biodistribution.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations on the cardiovascular system
Curcumin encapsulated in carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles conjugated to a myocyte-specific homing peptide has been found to increase the cardiac bioavailability of curcumin. The formulation has also been found to improve cardiac function by reducing the expression of hypertrophy marker genes and apoptotic mediators.
Several curcumin nanoformulations, such as hyaluronic acid-based nanocapsules, nanoparticles encapsulated in PLGA or nanoemulsion systems, have been found to increase the aqueous solubility of curcumin and subsequently prevent hypertension in animals. Similar cardio-protective effects have been observed using nanocurcumin polymer-based nanoparticles and curcumin and nisin-based polylactic acid nanoparticles. These formulations have been found to prevent myocardial damage and improve cardiac muscle functions.
Effects of curcumin nanoformulations on the brain
Curcumin complexed with galactomannans has been found to have better blood-brain barrier permeability and higher efficacy in preventing neuroinflammation, anxiety, fatigue, and memory loss in both humans and animals.
Curcumin-laden liposomes have been found to exert anti-amyloidogenic and anti-inflammatory effects in animal and cellular models of Alzheimer’s disease. Curcumin’s preventive activities against Alzheimer’s disease are associated with its ability to reduce amyloid-beta production and tau aggregation, which are major hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease.
However, clinical trials involving patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease could not find any beneficial effect of curcumin in reducing disease biomarkers and improving cognitive functions.
A recent clinical trial involving non-demented adults, on the other hand, has shown that oral curcumin treatment can improve memory and reduce amyloid and tau accumulation in the amygdala and hypothalamus.


