The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the importance of being prepared with drug interventions to contain viral outbreaks that can otherwise have devastating consequences. In preparing for the next pandemic—or Disease X, there is an urgent need for versatile platform technologies that could be repurposed upon short notice to combat infectious outbreaks.
A team of researchers, led by Assistant Professor Minh Le from the Institute for Digital Medicine (WisDM) and Department of Pharmacology at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), discovered that nano-sized particles released by cells, termed “extracellular vesicles” (EVs), can curb the viral infectivity of SARS-CoV-2—its wild type and variant strains—and potentially other infectious diseases.
Asst Prof Le said, “Our study showed that these cell-derived nanoparticles are effective carriers of drugs that target viral genes precisely. These EVs are, therefore, an efficient tool for therapeutic intervention in patients who are infected with COVID-19 or other infectious diseases.”
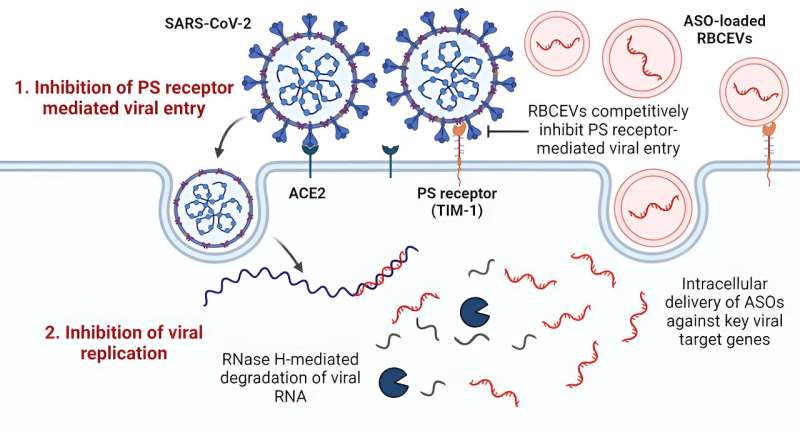
The study, conducted in collaboration with NUS Medicine’s Biosafety Level 3 (BSL3) Core Facility, the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore at National University of Singapore, and the School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences at Nanyang Technological University (NTU), demonstrated potent inhibition of COVID-19 infection in laboratory models using a combination of EV-based inhibition and anti-sense RNA therapy mediated by antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs).
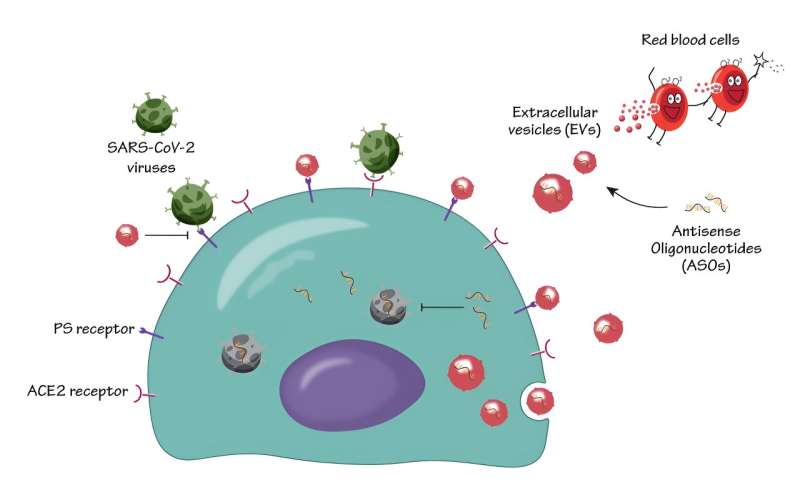
A versatile tool that can be applied to any gene of interest, ASOs can recognize and bind to complementary regions of target RNA molecules and induce their inhibition and degradation.
In the study, published in ACS Nano, the authors utilized human red blood cell-derived EVs to deliver ASOs to key sites infected with SARS-CoV-2, resulting in efficient suppression of SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication.
The researchers also discovered that EVs exhibited distinct antiviral properties, capable of inhibiting phosphatidylserine (PS) receptor-mediated pathways of viral infection—a key pathway utilized by many viruses to facilitate viral infection. These viral inhibitory mechanisms were applicable to multiple variants of SARS-CoV-2, including the delta and omicron strains, ensuring their broad effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The results from the study point to anti-sense RNA therapy with ASOs as a potentially effective approach that could serve to combat future viral outbreaks. The platform that was developed to deliver ASOs through EVs to target the SARS-CoV-2 viral genes can be readily applied to treat other viral infections by replacing the ASO sequences with those complementary to the target viral genes.
Asst Prof Le and her graduate students Migara Jay and Gao Chang, the first authors of the study, are currently developing more potent combinations of ASOs with the help of artificial intelligence prediction models to achieve enhanced viral inhibition. This collaborative effort includes a partnership with the research teams of Associate Professor Edward Chow from WisDM, NUS Medicine, and NUS Medicine’s BSL3 Core Facility.
Associate Professor Justin Chu, Director of the BSL3 Core Facility at NUS Medicine and co-author of the study, added, “This remarkable extracellular vesicle-based delivery platform technology coupled with anti-viral therapy is highly promising to combat a broad range of viruses and even Disease X.”
The latter is a general description of emerging and unknown infectious threats, such as novel coronaviruses. The term was used to alert and encourage the development of platform technologies, including vaccines, drug therapies, and diagnostic tests, which could be quickly customized and then deployed against future epidemic and pandemic outbreaks. Assoc Prof Chu is also from the Infectious Diseases Translational Research Programme at NUS Medicine.
Professor Dean Ho, Provost’s Chair Professor and Director of WisDM at NUS Medicine, said, “This work brings the scalable and well-tolerated extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery platform an important step closer towards clinical validation studies.”