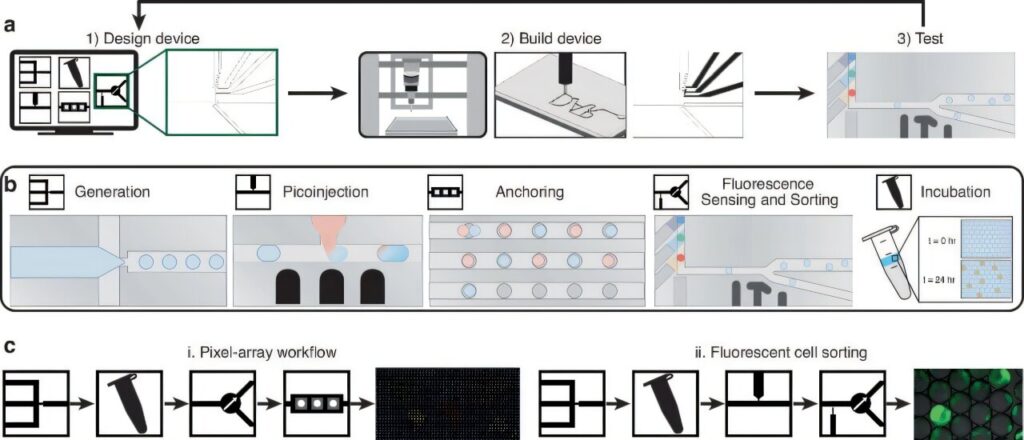
Researchers have developed a freely available droplet microfluidic component library, which promises to transform the way microfluidic devices are created. This innovation, based on low-cost rapid prototyping and electrode integration, makes it possible to fabricate microfluidic devices for under $12 each, with a full design-build-test cycle completed within a single day. The components are biocompatible, high-throughput, and capable of performing multistep workflows, such as droplet generation, sensing, sorting, and anchoring, all critical for automating microfluidic design and testing.
Microfluidics, particularly droplet-based systems, has become a promising technology for diverse fields, including protein engineering, single-cell sequencing, and nanoparticle synthesis. However, the traditional methods of fabricating microfluidic devices—typically using PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane)—are time-consuming and costly, often requiring cleanroom facilities or external vendors.
While alternatives like laser cutting and 3D printing have been explored, these methods often suffer from limitations in resolution, material compatibility, and scalability. As a result, there has been an urgent need for a more efficient, cost-effective, and accessible fabrication method to help propel innovation in microfluidic technology.
A team of researchers from Boston University has now published a study in Microsystems & Nanoengineering, detailing the development of a novel droplet microfluidic component library. This study introduces a rapid, low-cost method for fabricating microfluidic devices, essential for democratizing high-throughput biological and chemical screening.
These devices are not only biocompatible but are designed to perform complex workflows, such as fluorescent cell sorting and pixel array generation. A key innovation of the library is the ability to generate “signatures”—visual confirmations of droplet processing accuracy—which has applications as a diagnostic tool for ensuring quality control and troubleshooting during multistep workflows.
Dr. Douglas Densmore, a co-author of the study, remarked, “This new automation focused approach for fabricating droplet microfluidic devices is a significant advancement. By drastically reducing both the cost and time required for device production, we can now rapidly prototype and test new designs in standardized ways amenable to computer-aided design. This opens up numerous possibilities for high-throughput applications in biological and chemical research, making sophisticated microfluidic technology more accessible to a broader range of scientists and engineers.”
The implications of this microfluidic component library are far-reaching. By enabling rapid iteration and testing of initial designs, the technology cuts down on both the time and cost traditionally required for device fabrication. This is particularly valuable for large-scale dataset generation, which is key to advancing computer-aided design (CAD) tools for microfluidics.
The ability to generate and analyze complex droplet arrays also holds the potential to revolutionize biological and chemical analyses, paving the way for breakthroughs in areas such as protein engineering, genetic circuit analysis, and more. With this new development, the future of microfluidic technology appears brighter than ever.
Provided by
Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences