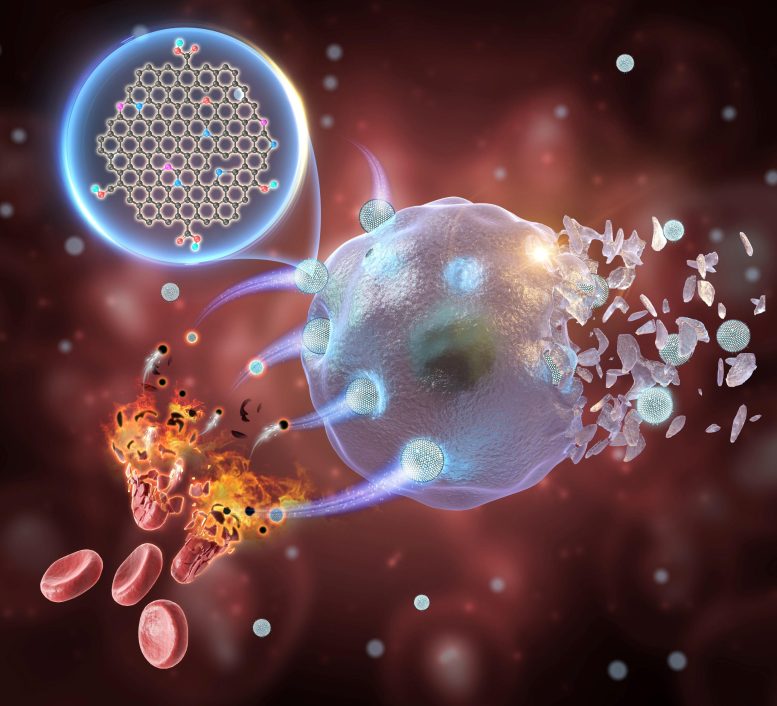
Schematic illustration showing the role of GQDs, derived from erythrocyte membranes, as peroxidase–mimic enzyme for tumor catalytic therapy. Credit: FHIPS
A team led by Professor Wang Hui at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed a metal-free nanozyme using graphene quantum dots (GQDs). This innovation is aimed at enhancing the effectiveness of tumor chemodynamic therapy (CDT).
The study was published in the journal Matter.
GQDs represent a promising and cost-effective means of addressing the toxicity concerns associated with metal-based nanozymes in tumor CDT. However, the limited catalytic activity of GQDs has posed significant challenges for their clinical application, particularly under challenging catalytic conditions.
“The obtained GQDs, which are made from red blood cell membranes, are highly effective in treating tumors with few side effects,” said LIU Hongji, a member of the research team. “One of the advantages is that they are metal-free. In addition, they function as excellent peroxidase-like biocatalysts.”
Enhancing Catalytic Performance
To enhance the catalytic performance of the GQD-based nanocatalytic adjuvant, the researchers rationally designed GQDs using a diatomic doping strategy. The synergistic electron effect of introducing nitrogen and phosphorus into GQDs can generate highly localized states near the Fermi level, thus enabling efficient enzymatic activity compared to single heteroatom doping.
The obtained GQDs, derived from erythrocyte membranes, have been shown to possess impressive peroxidase-mimicking activity. As a result, the GQDs are highly effective at inducing apoptosis and ferroptosis of cancer cells in vitro. They also selectively target tumors, with a tumor inhibition rate as high as 77.71% for intravenous injection and 93.22% for intratumoral injection, with no off-target side effects.
This drug-free, target-specific, and biologically benign nanozyme has great potential as a potent biocatalyst for use in safe cancer treatment.
Reference: “Graphene quantum dots as metal-free nanozymes for chemodynamic therapy of cancer” by Hongji Liu, Zhiming Deng, Zonghui Zhang, Wenchu Lin, Miqin Zhang and Hui Wang, 10 January 2024, Matter.
DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2023.12.005

