Polarized light waves spin clockwise or counterclockwise as they travel, with one direction behaving differently than the other as it interacts with molecules. This directionality, called chirality or handedness, could provide a way to identify and sort specific molecules for use in biomedicine applications, but researchers have had limited control over the direction of the waves—until now.
Using metamaterials, a team of electrical engineering researchers from Penn State and the University of Nebraska-Lincoln (UNL) created an ultrathin optical element that can control the direction of polarized electromagnetic light waves. This new control allows researchers to not only direct the light’s chirality, but also to identify the chirality of molecules by determining how polarized light interacts with them.
Identifying the chirality of molecules can reveal critical information about how they will interact with other systems, such as whether specific drugs will help heal diseased or damaged tissue without harming healthy cells. The researchers have published their findings in Nature Communications.
Chirality refers to mirror images, like left and right hands joining in a handshake, explained Christos Argyropoulos, associate professor of electrical engineering at Penn State and co-corresponding author on the paper. In physics, among other responsibilities, chirality influences the direction that light waves spin.
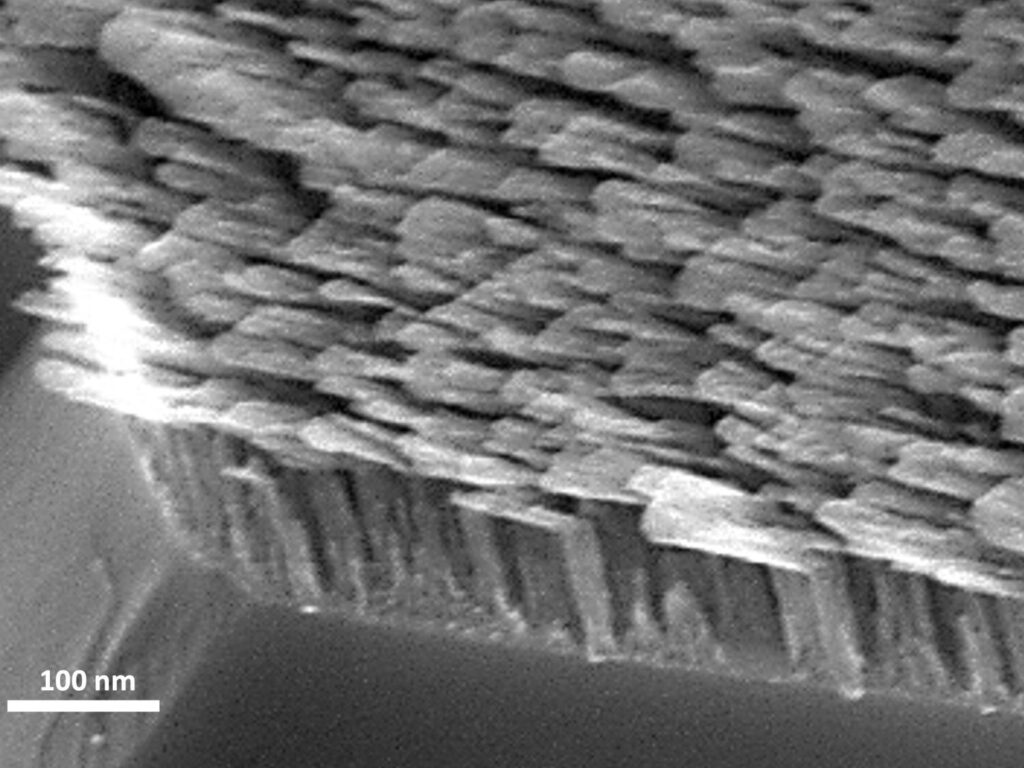
Argyropoulos and his colleagues fabricated an optical element, akin to a glass slide, that uses a forest of tiny, antenna-like nanorods that together create a metamaterial—or material engineered to have specific properties not typically found in nature—able to control the spin of light. The metamaterial nanorods appear to be shaped like the letter “L” when seen at the nanoscale.
“When the light-matter interaction is mediated by the metamaterials, you can image a molecule and identify its chirality by inspecting how chiral light interacts with it,” Argyropoulos said.
Researchers at UNL used an emerging fabrication approach called glancing angle deposition to fabricate the optical element out of silicon.
“Silicon does not substantially dissipate the incident light that was problematic with metal, which we used in previous attempts to create the element,” said Ufuk Kilic, a research professor at UNL and co-corresponding author on the paper. “And silicon allowed us to adjust the shape and length of the nanopillars on the platform, which in turn allows us to change how we control the light.”
Identifying the chirality of molecules can have wide-ranging impacts in biomedicine, particularly in pharmaceutical drugs, which sometimes have right- or left-handed chirality, Argyropoulos explained. While a right-handed molecular structure can be effective at treating disease, the same molecule with a left-handed structure can be toxic to healthy cells.
Argyropoulos mentioned the classic example of thalidomide, a drug with a chiral structure that was prescribed to women to treat morning sickness between 1957 and 1962. The right-handed molecule could appease nausea but was highly toxic to developing fetuses and caused birth defects for thousands of babies around the world.
The optical element, Argyropoulos said, can quickly image the molecular structure of pharmaceuticals, allowing scientists to better understand the nuances of drug behavior.
Additionally, the optical element can be used to create right- or left-handed electromagnetic waves, Argyropoulos said, which are necessary for the development and maintenance of classical and quantum communications systems, like encrypted Wi-Fi and cell phone service.
“Previously, for optical communication systems, you needed big, bulky devices that only operated at one frequency,” Argyropoulos said. “This new optical element is lightweight and easily tunable to multiple frequencies.”