The human brain has billions of neurons. Working together, they enable higher-order brain functions such as cognition and complex behaviors. To study these higher-order brain functions, it is important to understand how neural activity is coordinated across various brain regions.
Although techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) are able to provide insights into brain activity, they can show only so much information for a given time and area. Two-photon microscopy involving the use of cranial windows is a powerful tool for producing high-resolution images, but conventional cranial windows are small, making it difficult to study distant brain regions at the same time.
Now, a team of researchers led by the Exploratory Research Center on Life and Living Systems (ExCELLS) and the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS) have introduced a new method for in vivo brain imaging, enabling large-scale and long-term observation of neuronal structures and activities in awake mice.
This method is called the “nanosheet incorporated into light-curable resin” (NIRE) method, and it uses fluoropolymer nanosheets covered with light-curable resin to create larger cranial windows.
“The NIRE method is superior to previous methods because it produces larger cranial windows than previously possible, extending from the parietal cortex to the cerebellum, utilizing the biocompatible nanosheet and the transparent light-curable resin that changes in form from liquid to solid,” says lead author Taiga Takahashi of the Tokyo University of Science and ExCELLS.
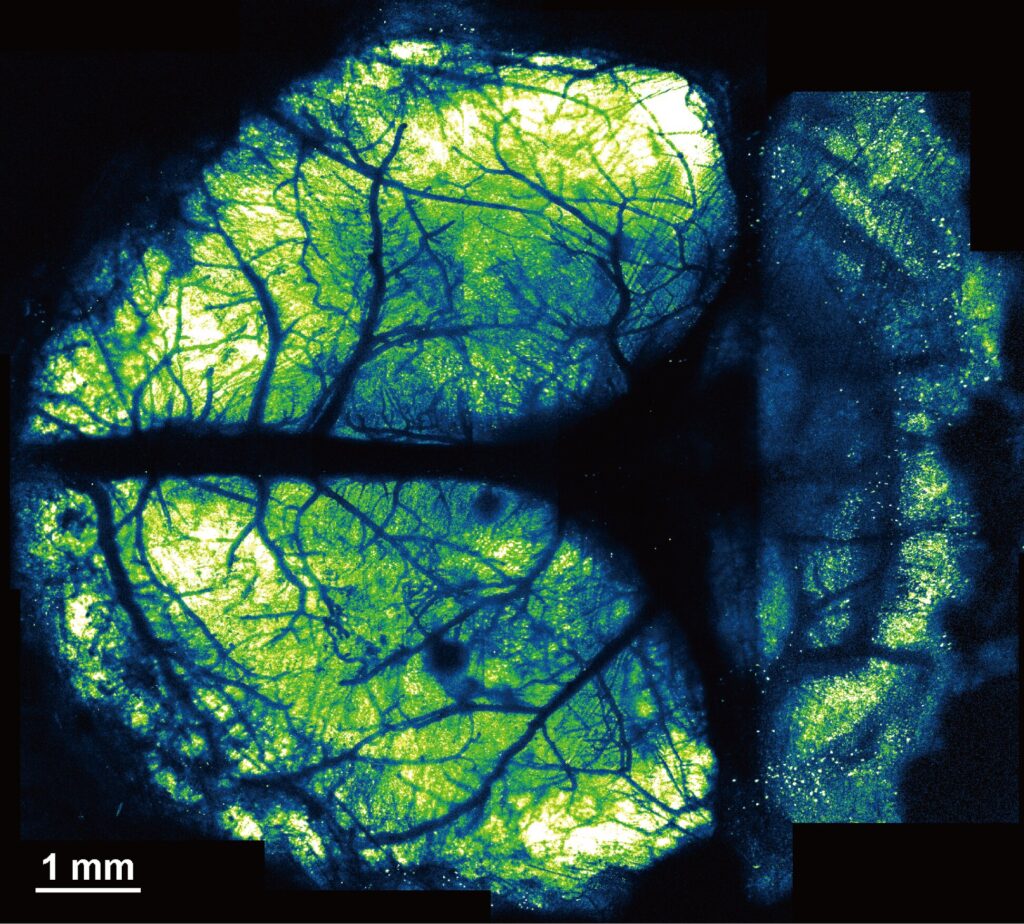
In the NIRE method, light-curable resin is used to fix polyethylene-oxide–coated CYTOP (PEO-CYTOP), a bioinert and transparent nanosheet, onto the brain surface. This creates a “window” that fits tightly onto the brain surface, even the highly curved surface of the cerebellum, and maintains its transparency for a long time with little mechanical stress, allowing researchers to observe multiple brain regions of living mice.
“Additionally, we showed that the combination of PEO-CYTOP nanosheets and light-curable resin enabled the creation of stronger cranial windows with greater transparency for longer periods of time compared with our previous method. As a result, there were few motion artifacts, that is, distortions in the images caused by the movements of awake mice,” says Takahashi.
The cranial windows allowed for high-resolution imaging with sub-micrometer resolution, making them suitable for observing the morphology and activity of fine neural structures.
“Importantly, the NIRE method enables imaging to be performed for a longer period of more than 6 months with minimal impact on transparency. This should make it possible to conduct longer-term research on neuroplasticity at various levels—from the network level to the cellular level—as well as during maturation, learning, and neurodegeneration,” explains corresponding author Tomomi Nemoto at ExCELLS and NIPS.
This study is a significant achievement in the field of neuroimaging because this novel method provides a powerful tool for researchers to investigate neural processes that were previously difficult or impossible to observe. Specifically, the NIRE method’s ability to create large cranial windows with prolonged transparency and fewer motion artifacts should allow for large-scale, long-term, and multi-scale in vivo brain imaging.
“The method holds promise for unraveling the mysteries of neural processes associated with growth and development, learning, and neurological disorders. Potential applications include investigations into neural population coding, neural circuit remodeling, and higher-order brain functions that depend on coordinated activity across widely distributed regions,” says Nemoto.
In sum, the NIRE method provides a platform for investigating neuroplastic changes at various levels over extended periods in animals that are awake and engaged in various behaviors, which presents new opportunities to enhance our understanding of the brain’s complexity and function.