A joint research team has developed a biotemplating method that utilizes specific internal proteins in biological samples and has high tunability. The study is published in Advanced Science.
Existing biotemplate methods mainly utilize only the external surface of biological samples or have limitations in utilizing the structure-function correlation of various biological structures due to limited dimensions and sample sizes, making it difficult to create functional nanostructures.
To solve this problem, the research team studied a way to utilize various biological structures within the cells while retaining high malleability.
As a result of the research, the team developed the conversion to advanced materials via labeled Biostructure, shortened as CamBio, that can selectively synthesize nanostructures with various specificities and sizes from specific protein structures in biological samples composed of various proteins.
The CamBio method secures high re-tunability of functional nanostructures that can be manufactured from biological samples by merging various manufacturing and biological technologies.
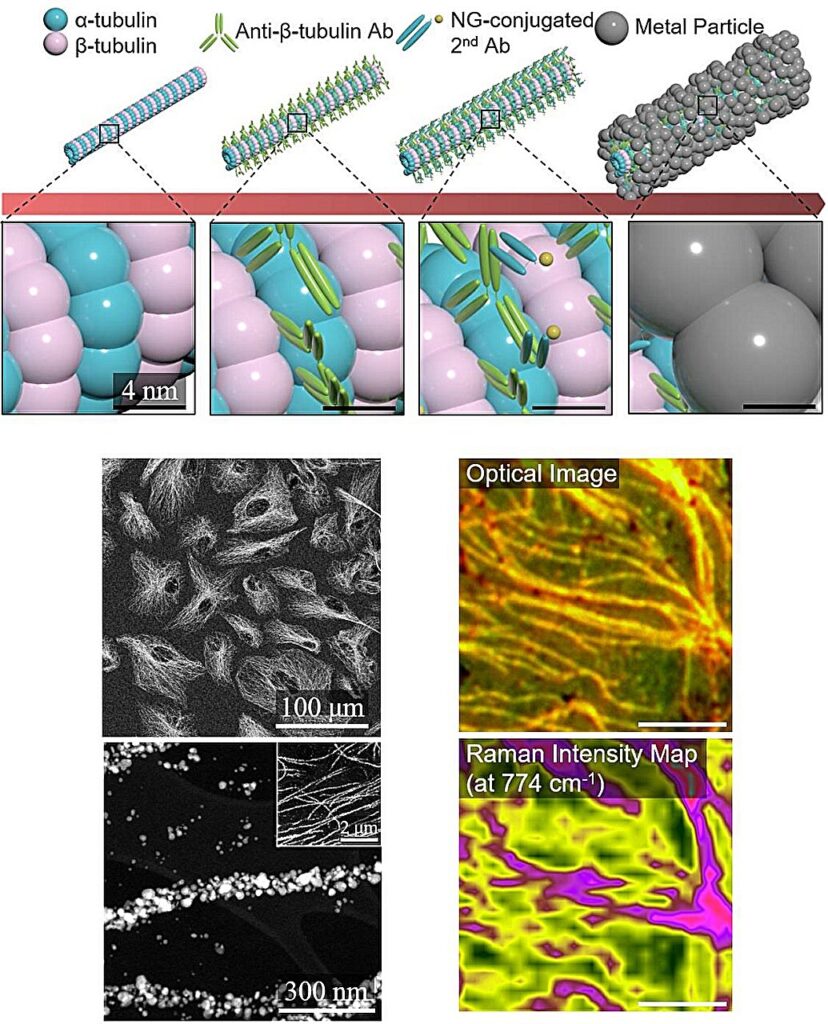
Through the technology of repeatedly attaching antibodies, arranging cells in a certain shape, and thinly slicing tissue, the functional nanostructures made with CamBio showed improved performance on the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrate used for material detection.

The research team found that the nanoparticle chains made using the intracellular protein structures through the process of repeated labeling with antibodies allowed easier control, and improved SERS performance by up to 230%.
The research team included Professors Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung, and first authors Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song, along with Dr. Chang Woo Song, and Dr. Seunghee Cho of KAIST.
In addition, the research team expanded from utilizing the structures inside cells to obtaining samples of muscle tissues inside meat using a cryosectioner and successfully producing a substrate with periodic bands made of metal particles by performing the CamBio process. This method of producing a substrate not only allows large-scale production using biological samples, but also shows that it is a cost-effective method.
The CamBio developed by the research team is expected to be used as a way to solve problems faced by various research fields as it is to expand the range of bio-samples that can be produced for various usage.

The first author, Dae-Hyeon Song, “Through CamBio, we have comprehensively accumulated bioprototyping methods that can utilize more diverse protein structures.
“If combined with the latest biological technologies such as gene editing and 3D bioprinting and new material synthesis technologies, biostructures can be utilized in various fields of application.”