Water pollution from dyes used in textile, food, cosmetic and other manufacturing is a major ecological concern with industry and scientists seeking biocompatible and more sustainable alternatives to protect the environment.
A new study led by Flinders University has discovered a novel way to degrade and potentially remove toxic organic chemicals including azo dyes from wastewater, using a chemical photocatalysis process powered by ultraviolet light.
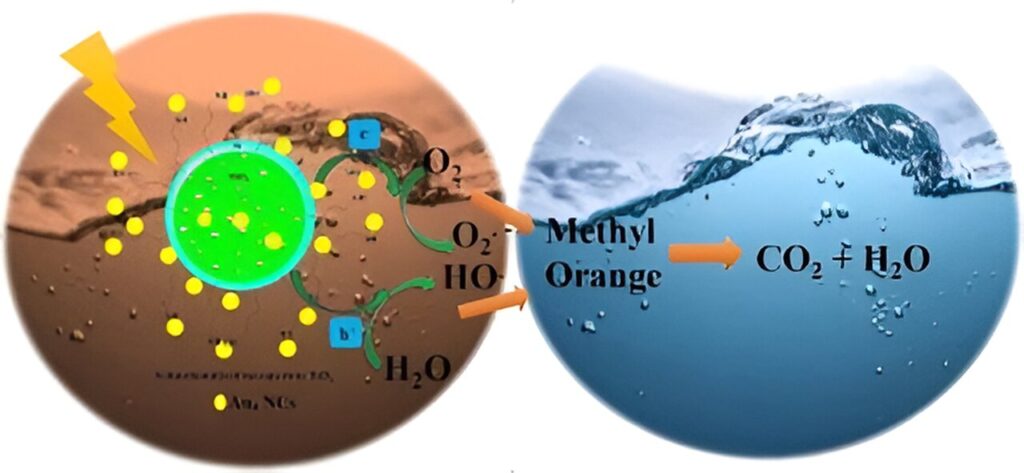
Professor Gunther Andersson, from the Flinders Institute for NanoScale Science and Technology, says the process involves creating metallic ‘clusters’ of just nine gold (Au) atoms chemically ‘anchored’ to titanium dioxide which in turn drives the reaction by converting the energy of absorbed UV light.
The gold nanocluster cocatalysts enhance the photocatalytic work of the titanium dioxide and reduce the time required to complete the reaction by a factor of six, according to the new journal article in Solar RRL.
“These types of heterogeneous semiconductor-mediated photocatalysis systems provide a significant advantage over other advanced chemical processes,” says Professor Andersson, from the College of Science and Engineering.
“It can facilitate the mineralization of a large range of organic pollutants, like azo dyes, into water and carbon dioxide molecules with a high degradation efficiency.”
A variety of physical, chemical and biological processes are currently used to remove carcinogenic and recalcitrant organic compounds from water.
A wide range of chemical industries, including dye manufacture, textile and cosmetics production, release toxic and non-biodegradable dyes into the environment. Nearly half of the dyes used in the textile and dye industry are azo dyes. Methyl orange is widely used as a water-soluble azo dye.
With this in mind, the Flinders University nanotech researchers have also demonstrated the usefulness of this gold cluster cocatalyst and modified semiconductors for synthesis of the novel photocatalysis systems for degradation of methyl orange.
This study, published in Applied Surface Science, tested the photocatalysis in a vortex fluidic device developed at Flinders University in Professor Colin Raston’s nanotechnology laboratory.
Co-author Flinders Ph.D. Dr. Anahita Motamedisade says traditional wastewater treatment methods often do not effectively remove dangerous contaminants from wastewater.
“The reason for this is that some chemicals, especially those with aromatic rings, are resistant to chemical, photochemical and biological degradation,” says Dr. Motamedisade, who is now a research fellow at the Center for Catalysis and Clean Energy at Grifffith University.
“In addition, they generate dangerous by-products by oxidizing, hydrolyzing, or undergoing other chemical reactions of synthetic dyes containing wastewater, which are detectable wherever they are disposed of.
“We hope to build onto these more sustainable and thorough photocatalytic degradation processes to help completely remove the toxins and tackle this global problem.”
The research was inspired by Dr. Motamedisade’s Ph.D. research which includes better ways to treat winery wastewater.