Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections that cannot be treated by any known antibiotics pose a serious global threat. Publishing in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition, a Chinese research team has now introduced a method for the development of novel antibiotics to fight resistant pathogens. The drugs are based on protein building blocks with fluorous lipid chains.
Antibiotics are often prescribed far too readily. In many countries they are distributed without prescriptions and administered in factory farming: prophylactically to prevent infections and enhance performance. As a result, resistance is on the rise—increasingly against reserve antibiotics as well. The development of innovative alternatives is essential.
It is possible to learn some lessons from the microbes themselves. Lipoproteins, small protein molecules with fatty acid chains, are widely used by bacteria in their battles against microbial competitors. A number of lipoproteins have already been approved for use as drugs.
The common factors among the active lipoproteins include a positive charge and an amphiphilic structure, meaning they have segments that repel fat and others that repel water. This allows them to bind to bacterial membranes and pierce through them to the interior.
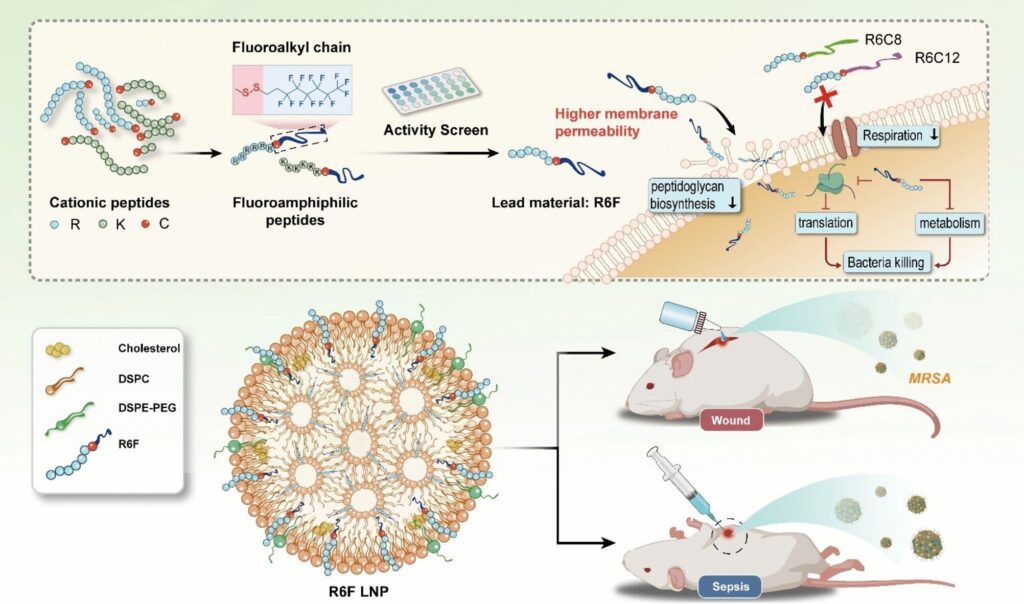
The team led by Yiyun Cheng at East China Normal University in Shanghai aims to amplify this effect by replacing hydrogen atoms in the lipid chain with fluorine atoms. These make the lipid chain simultaneously water-repellant (hydrophobic) and fat-repellant (lipophobic). Their particularly low surface energy strengthens their binding to cell membranes while their lipophobicity disrupts the cohesion of the membrane.
The team synthesized a spectrum (substance library) of fluorous lipopeptides from fluorinated hydrocarbons and peptide chains. To link the two pieces, they used the amino acid cysteine, which binds them together via a disulfide bridge.
The researchers screened the molecules by testing their activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a widespread, highly dangerous strain of bacteria that is resistant to nearly all antibiotics. The most effective compound they found was “R6F,” a fluorous lipopeptide made of six arginine units and a lipid chain made of eight carbon and 13 fluorine atoms. To increase biocompatibility, the R6F was enclosed within phospholipid nanoparticles.
In mouse models, R6F nanoparticles were shown to be very effective against sepsis and chronic wound infections by MRSA. No toxic side effects were observed.
The nanoparticles seem to attack the bacteria in several ways: they inhibit the synthesis of important cell-wall components, promoting collapse of the walls; they also pierce the cell membrane and destabilize it; disrupt the respiratory chain and metabolism; and increase oxidative stress while simultaneously disrupting the antioxidant defense system of the bacteria.
In combination, these effects kill the bacteria—other bacteria as well as MRSA. No resistance appears to develop.
These insights provide starting points for the development of highly efficient fluorous peptide drugs to treat multi-drug resistant bacteria.