During the first 72 hours in particular, extracellular vesicles—nanoparticles enclosed in cell membranes—play a significant role in the embryonic development of zebrafish.
This is the result of a study conducted at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) and Universitätsklinikum Erlangen (UKER), which has now been published in Cell Communication and Signaling.
For the first time, researchers were able to study the dynamics of extracellular vesicles over a period of four days in order to discover more about their significance for cell differentiation and organ formation. The results show potential for the field of human medicine, since extracellular vesicles could be used as a targeted drug delivery system.
Extracellular nanoparticles play an important role in cell differentiation and the coordinated growth of organs in the embryonic phase. These also include something known as extracellular vesicles (EV) that are released by cells and that are enclosed in a double membrane.
They transport messenger substances such as proteins and messenger RNA and thus enable cells to communicate with each other. A distinction is made between small and large extracellular vesicles (smallEVs and largeEVs).
“This classification not only has something to do with the size of the particles, but also with the different ways they are formed and their functions,” explains Dr. Linda-Marie Mulzer, who is a physician in child and adolescent medicine at UKER and the lead author of the study.
Two types of extracellular vesicles are essential for organ formation
To date, there has been little research on which phases and processes require EVs, in organ formation in particular. This is a gap that researchers at FAU and UKER hope to close by investigating the dynamics of vesicles in zebrafish.
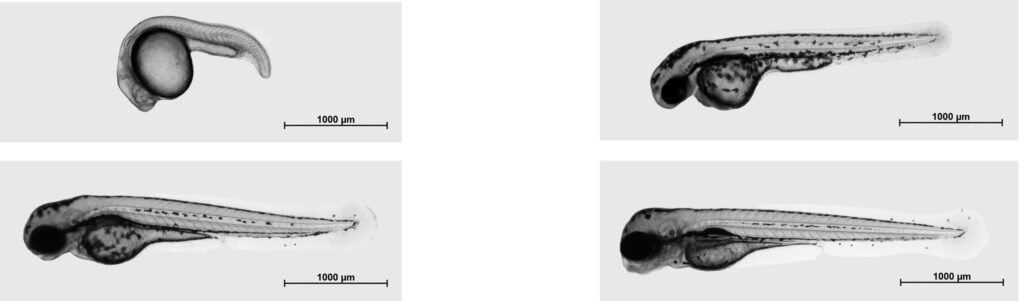
“Zebrafish larvae are particularly suitable for our studies because they are almost completely transparent, allowing us to observe the development of their inner organs,” explains Mulzer. The larvae were examined for the presence of EV at 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours after fertilization using flow cytometry, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and western blotting (WB) allowing the researchers to analyze the EV and determine their size and quantity.
Mulzer says, “This is the first study to present microscopic images of vesicles of entire zebrafish. It has enabled us to make a clear distinction between smallEVs and largeEVs and demonstrate that at least two different types of EVs are involved in zebrafish embryogenesis.”
Another significant finding of the study is that the overall number of EVs rose significantly during the first 72 hours of embryogenesis, and at a rate much higher than could be expected when considering the increase in length of the fish larvae. At the same time, the average size of the smallEVs also increased during this time.
“Since most organs are formed during the first three days after fertilization and maturity and growth mostly occur afterwards, the increasing number of EVs suggests they have an important role during organ formation in zebrafish,” explains Mulzer. “The increase in size can be explained with an increase in transport capacity because the metabolic activity in the cells increases during this phase.”
The researchers consider their study to be the start of a more in-depth analysis, in particular of the specific functions of the EVs. “Our experiments were not yet able to show which substances the EVs are loaded with. In addition, we are quite a way away from being able to decipher and describe all subtypes of EVs,” says Mulzer.
If it is possible to determine which organs are specifically targeted by the relevant EVs, this may open the door to new types of therapies—such as the suppression of unwanted cell growth or the targeted treatment of organs with effective drugs.