In a new study, scientists at Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine found a promising new way to treat a type of oral cancer known as oral squamous cell carcinoma. The method specifically targets the cancer cells through a combination of nitric oxide gas therapy and nanocatalytic therapy, killing them more effectively and with fewer side effects. The study was published in Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
Oral squamous cell carcinoma is a very aggressive cancer that tends to spread quickly and to reappear after treatment. Traditional treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, often have serious side effects, including trouble speaking or eating and painful conditions like mouth sores and dry mouth.
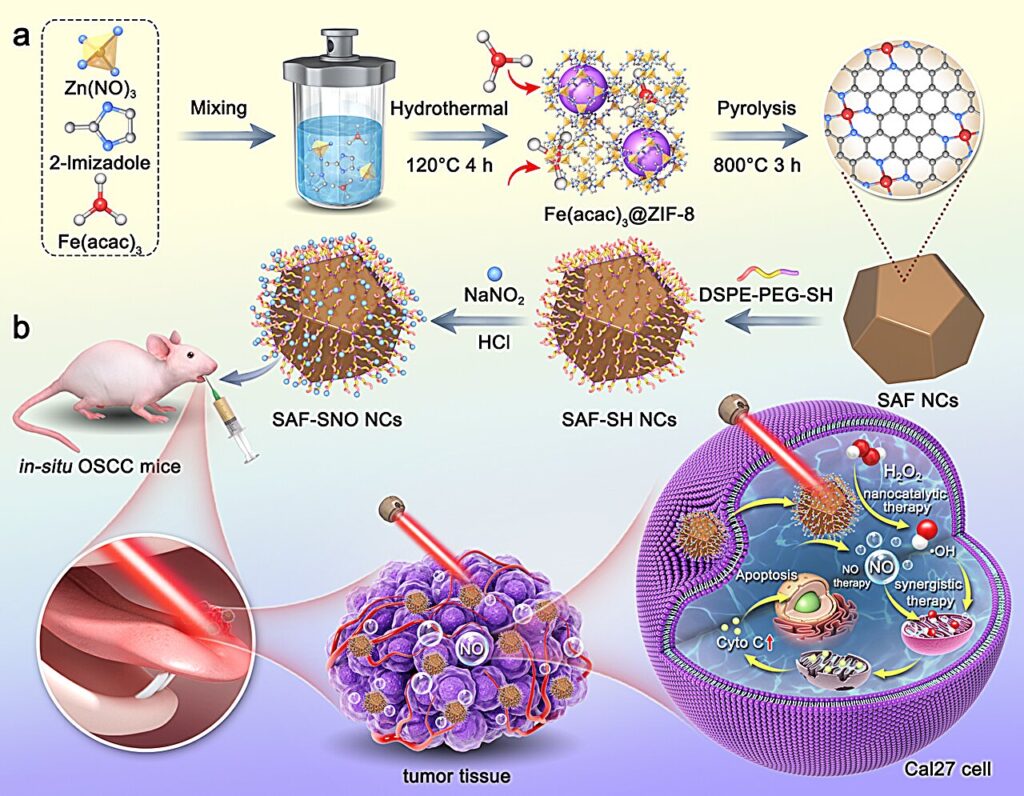
Researchers are trying to develop better treatments that wouldn’t have such harsh side effects. One approach relies partly on nanocatalysts, tiny particles measuring 1 to 100 nanometers in size that are used to accelerate chemical reactions.
“We created tiny iron particles composed of individual iron atoms, designed to interact with hydrogen peroxide—a substance found in elevated levels inside tumor cells,” explains Professor Ping Xiong, who led the study. “These atoms use a chemical process called the Fenton reaction, where the iron atoms act as catalysts to convert hydrogen peroxide into highly toxic hydroxyl radicals.”
Hydroxyl radicals are extremely reactive and cause intense oxidative stress by damaging cellular components such as DNA and proteins. The iron particles also carried molecules that released nitric oxide gas when activated by near-infrared laser light. The nitric oxide gas amplified the effect of the hydroxyls by triggering apoptosis, a controlled form of cell death crucial for removing damaged cells.
In animal model experiments, a single dose of treatment combined with a laser pulse was found to suppress tumors by around 85.5%, suggesting that the treatment is very effective. “This treatment is highly specific to cancer cells, reducing damage to healthy tissues and minimizing side effects, which makes it both more efficient and better tolerated by the body,” says Yuting Xie, one of the study’s authors.
One major difficulty was ensuring that the infrared laser targeted only the tumor, especially in hard-to-reach areas like the sides and bottom of the tongue. The team is exploring ways to improve the precision of the laser treatment to avoid inadvertent damage to the surrounding healthy tissues, which could result in unwanted side effects.
One approach being investigated involves developing nanocatalysts that would be administered through an intravenous injection, which could enhance the targeting by interacting with the laser in a more controlled manner.
The researchers are also working on strategies to prevent the cancer from spreading or returning after treatment. By further refining these technologies, they hope to create a more effective and targeted treatment option for this invasive cancer.