Research into artificial intelligence (AI) network computing has made significant progress in recent years but has so far been held back by the limitations of logic gates in conventional computer chips. Through new research published in The European Physical Journal D, a team led by Aijin Zhu at Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China, introduced a graphene-based optical logic gate, which addresses many of these challenges.
The design could lead to a new generation of computer chips that consume less energy while reaching higher computing speeds and efficiencies. This could, in turn, pave the way for the use of AI in computer networks to automate tasks and improve decision-making—leading to enhanced performance, security, and functionality.
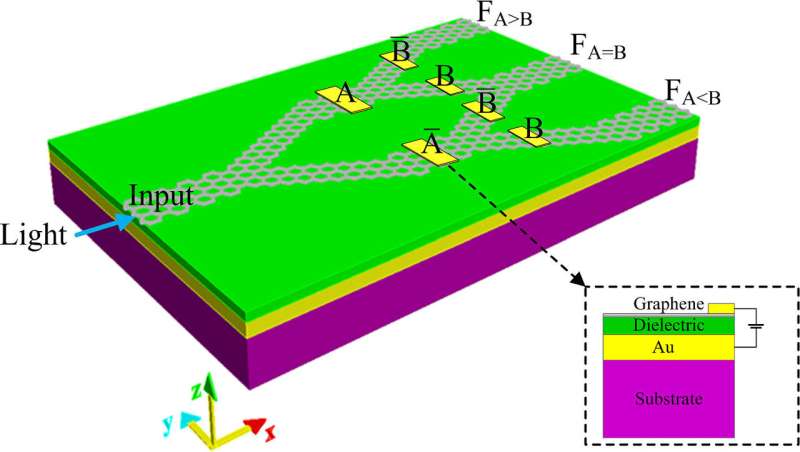
There are many advantages to microchips whose component logic gates exchange signals using light instead of electrical current. However, current designs are often bulky, somewhat unstable, and vulnerable to information loss.
In their paper, Zhu’s team introduced a graphene-based alternative composed of Y-shaped graphene nanoribbons bonded on top of a layer of insulation. This design is ideal for hosting plasmon waves, collective oscillations of electrons that arise at the interface between the graphene and the insulating medium. They can be triggered by the light waves in incoming optical signals and can also generate outgoing signals themselves after the information is processed by the logic gate.
Since surface plasmon wavelengths are shorter than those of optical light waves, the researchers show that their setup can become far more compact than previous designs of optical logic gates. Their device can be switched on and off using an external voltage, which manipulates the energy levels at which electrons in graphene are available for conveying electrical current.
In their experiments, Zhu’s team achieved an impressively high ratio between the power level of their gate’s ‘on’ and ‘off’ states, where it transmits and blocks data, respectively. As well as outperforming previous optical logic gates, their design also benefits from a small size, low loss of information, and high stability.