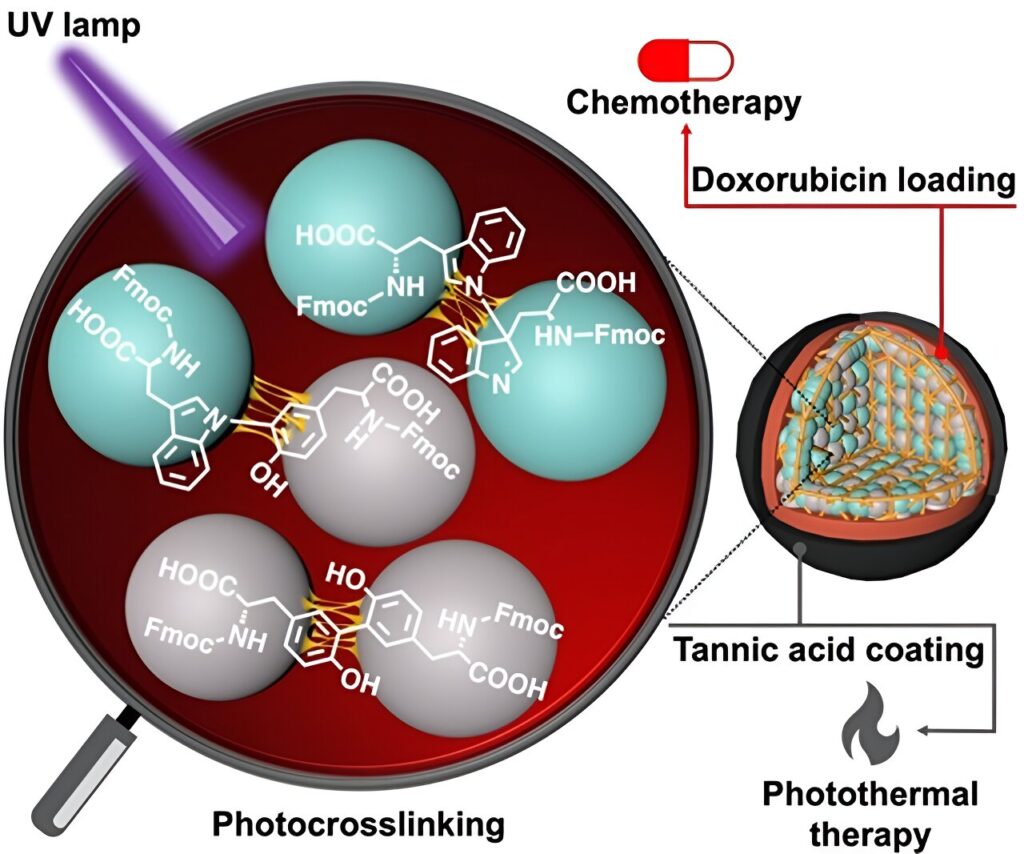
Amino acids, such as tyrosine and tryptophan, are the fundamental building blocks that make up proteins. These biomolecules have different chemical groups on each end and side chain, and so, have the natural ability to form a chain through the formation of an amide (peptide) bond. However, such linkages are weak and easily degraded under physiological conditions. This is where the Fmoc-protected amino acids come into the picture.
In a new study now, a research team led by Dr. Eijiro Miyako, Associate Professor, Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST) and Dr. Alberto Bianco and Dr. Cécilia Ménard-Moyon from the Center National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), France, employed ultraviolet light at 254 nm (leading to CBPUV nanoparticles) and riboflavin-mediated crosslinking at 365 nm (leading to CBPRibo nanoparticles) to crosslink the Fmoc-protected amino acids.
“Amino acids being the building blocks of proteins have numerous advantages, such as better biocompatibility. Therefore, we wanted to create novel self-assembled amino acid-based nanoparticles which can be triggered through multiple mechanisms,” says Dr. Eijiro Miyako. The findings of this study are published in Small.
The self-assembled amino acids were stably crosslinked dimers of Fmoc-Tyr-OH (Tyrosine) and Fmoc-Trp-OH (Tryptophan). Doxorubicin, an anticancer drug, was subsequently loaded into the crosslinked amino acid nanoparticles.
To increase the stability of the nanoparticles, the researchers used a tannic acid-Iron (Fe3+) complex (or TAF) as the outer layer of coating. This coating can degrade inside the cells through the glutathione enzymatic release or by pH difference in the tumor microenvironment. The tannic acid coating can be also used in photothermal anticancer therapy, where external light can increase the local temperature surrounding the cancer tissue, causing cancer cell death.
The synthesized nanoparticles were then extensively studied for their structural integrity, stability, and drug release under different pH conditions. The functional profile, cellular uptake, and biocompatibility of self-assembled amino acid nanoparticles were then studied using cell culture techniques.
Finally, the anticancer efficacy of synthesized nanoparticles was analyzed in tumor-bearing mice. The combined approach of chemotherapy, due to doxorubicin action, and photothermal therapy thanks to the tannic acid coating, showed excellent anticancer activity.
Post crosslinking, the amino acid-based nanoparticles showed notable changes in color, size, absorbance, fluorescence, and thermal stability. Furthermore, CBPUV exhibited superior stability after crosslinking, compared to CBPRibo. CBPUV also consistently maintained its structure, while CBPRibo showed partial disassembly, forming hollow spheres.
Drug release study revealed minimal drug release under physiological pH (7.4), indicating that stable coating is crucial for in vivo delivery. At pH 5.5, incomplete coating degradation resulted in negligible drug release. However, the addition of glutathione (GSH) at pH 5.5 significantly boosted drug release by triggering TAF coating degradation, indicating GSH/pH responsiveness.
The combined acidic and GSH treatment intensified coating degradation. This responsive behavior enables controlled drug release in specific physiological conditions. Furthermore, in vitro assessments revealed concentration-dependent cytotoxicity and improved efficacy in combined chemo/photothermal therapy. In vivo studies on tumor-bearing mice showcased significant tumor growth inhibition, indicating promising anticancer effects without observed side effects.
Dr. Miyako said, “Nanotechnology holds promise of transforming basic laboratory science into a powerful tool for combating complex diseases like cancer. We are optimistic that this pioneering research will advance, potentially evolving into cutting-edge cancer treatment technology ready for clinical trials within ten years.”
Going ahead, the development of these self-assembled amino acid nanoparticles can help in fighting critical issues such as multi-drug resistance in cancer and improve the overall efficacy of treatment outcomes.