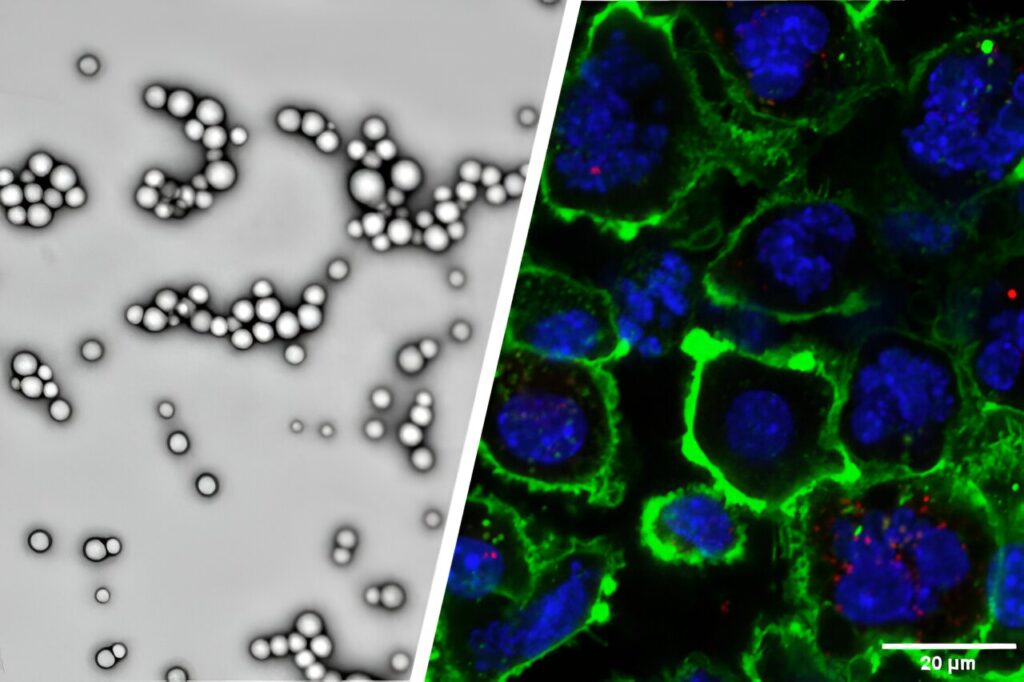
Purdue University researchers are developing and validating patent-pending poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid), or PLGA, nanoparticles modified with adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, to enhance immunotherapy effects against malignant tumors.
The nanoparticles slowly release drugs that induce immunogenic cell death, or ICD, in tumors. ICD generates tumor antigens and other molecules to bring immune cells to a tumor’s microenvironment. The researchers have attached ATP to the nanoparticles, which also recruits immune cells to the tumor to initiate anti-tumor immune responses.
Yoon Yeo leads a team of researchers from the College of Pharmacy, the Metabolite Profiling Facility in the Bindley Bioscience Center, and the Purdue Institute for Cancer Research to develop the nanoparticles. Yeo is the associate department head and Lillian Barboul Thomas Professor of Industrial and Molecular Pharmaceutics and Biomedical Engineering; she is also a member of the Purdue Institute for Drug Discovery and the Purdue Institute for Cancer Research.
The researchers validated their work using paclitaxel, a chemotherapy drug used to treat several types of cancers. They found that tumors grew slower in mice treated with paclitaxel enclosed within ATP-modified nanoparticles than in mice treated with paclitaxel in non-modified nanoparticles.
“When combined with an existing immunotherapy drug, the ATP-modified, paclitaxel-loaded nanoparticles eliminated tumors in mice and protected them from rechallenge with tumor cells,” Yeo said.
The research has been published in ACS Nano.
Challenges to systemic immunotherapy delivery
Immunotherapy is a promising approach to fighting cancer, but Yeo said it does not benefit a large population of patients because they do not have the powerful immune cells needed to combat tumors.
“Pharmacological agents to activate immune cells can directly be given to tumors,” Yeo said. “Then the immune system can fight not only the treated tumors but also nontreated tumors in distant locations as the activated immune cells circulate in the bloodstream.”
However, Yeo said most tumors with poor prognoses are not always locatable or accessible. Therefore, they may not be effectively treated by local therapy. She and her team envisioned systemic delivery of immunotherapy, but there are challenges.
“For successful systemic administration, active ingredients that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses need to be simultaneously present in tumors to exert concerted effects on the target,” Yeo said. “The ingredients also must maintain their activity until they reach tumors, but not cause toxic off-target effects. Moreover, the carriers traditionally used in local drug delivery offer limited utility in systemic application because they may not be compatible with blood components.”
Yeo and her colleagues used biocompatible polymeric nanoparticles to deliver immunotherapy compounds and modified them to safely activate the immune system.
“We employed poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid), or PLGA, nanoparticles based on the strong track record of the polymer in FDA-approved products and its routine use in the systemic delivery of poorly water-soluble drugs,” Yeo said.
Tests verified the ATP-modified PLGA nanoparticles were well tolerated in mice upon multiple systemic injections. They were able to recruit dendritic cells, the immune cells that recognize tumor antigens and bring specialized immune cells to fight off tumors.
“Moreover, the nanoparticles were shown to control the release of paclitaxel to minimize its systemic toxicity,” Yeo said.
The next development steps
Yeo and her colleagues will continue their work on the ATP-modified nanoparticles.
“We are currently working on improving the delivery of the nanoparticles to tumors and combining them with other treatments that will circumvent the resistance to the nanoparticle-delivered immunotherapy,” Yeo said. “To finance these efforts, we will apply for continued support from the National Institutes of Health. We are also open to industry partnerships to take this technology to the clinic.”