A perfect combination of fiber optics and micro/nanotechnology, optical micro/nanofiber (MNF) is a new type of micro/nano-waveguide structure developed in recent years.
Compared with standard fiber, MNF has a smaller diameter and larger core cladding refractive index contrast, so it offers unique optical properties, including low transmission loss, strong light-field constraint, large evanescent field, small bending radius, small mass, and compatibility with standard fiber.
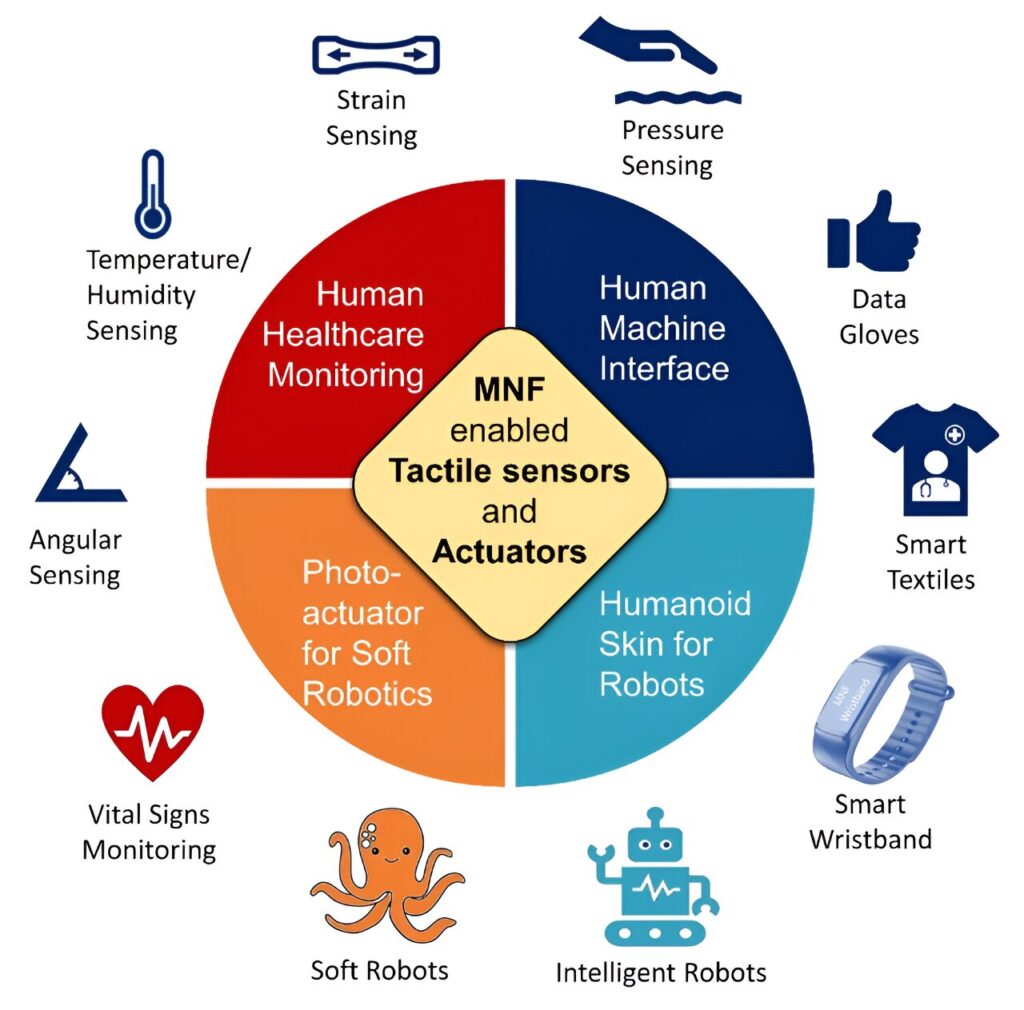
MNF-enabled flexible optoelectronic devices with high sensitivity, small size, and low power consumption have been widely used in the fields of tactile sensors and soft actuators. To date, flexible MNF sensors, also known as “optical skin,” have been used to monitor pressure, temperature, hardness, pulse and breathing with high sensitivity, fast response, and anti-electromagnetic interference.
In addition, the MNF-enabled soft actuators provide a new strategy for micromanipulation and micro-robotics. MNFs have unique properties in the field of flexible optoelectronics and have broad application prospects in the fields of machine haptics, human-computer interaction, medical monitoring, and micro-nano robots.
A review published in Opto-Electronic Science covers two parts of MNF-enabled tactile sensors and actuators. First, the manufacturing method for MNF tactile sensor is presented from the aspects of fiber drawing, polymer packaging, device preparation and system integration. Then, the review introduces structural design, sensing mechanism, performance characteristics and application fields, such as fingertip/radial pulse monitoring, data gloves, smart wristband, tactile textile and industrial/medical robots.
Mechanistically, MNF-enabled tactile sensors can be categorized into taper type (single-cone), double-cone type, resonator type, grating type, interferometer type and micro-coupler type according to their structures.
The sensing signal is extracted mainly through wavelength demodulation and intensity demodulation. Wavelength demodulation by tracking the movement of resonant wavelength is mainly used in WGM resonators, FP resonators, Theta resonators, Sagnac resonators, Fiber Bragg Grating, etc.
Intensity detection is a simpler detection method, which uses miniaturized semiconductor light source and photodiode to monitor the change of MNF’s transmittance, so as to realize the miniaturization of a sensing system and efficient acquisition of sensing signals.

The MNF-enabled data glove, smart wristband, smart textiles, proximity and tactile composite multi-parameter interactive interfaces have realized the systematic integration of light source, photo detectors, and MNF sensors. They are lightweight, sensitive, and have low power consumption and anti-electromagnetic interference in the field of human-computer interaction.
MNFs also have high compliance and a strong evanescent field, making MNF-enabled photoactuators with large angular deformation, stable for the safe clamping of small objects.

In summary, this paper reviews the cutting-edge progress and highlights of the research in MNF-enabled tactile sensors/actuators and looks forward to the great potential of applications in the fields of distributed sensing, soft actuators with the abilities of complex deformation and sensing, and AI-enhanced sensors/actuators.
Provided by
Compuscript Ltd