The Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai, in collaboration with the Australian National University, Canberra has demonstrated a novel way of steering a beam of relativistic electron pulses produced by an ultrahigh intensity, femtosecond laser. Their study is published in the journal Laser and Photonics Reviews.
Beams of high energy electrons are crucial for fundamental science and myriad applications and technologies, such as imaging, semiconductor lithography, material science and medical therapies. Typically, such beams are derived from accelerators—complex, expensive devices in large sizes and with sophisticated, high-power electrical and control systems. And each is geared towards operation in a certain regime of energies and currents, which is very difficult to modify at will.
High intensity femtosecond laser pulses have been driving electrons to very high energies reaching million and billion electron volts over length scales that are 100–1,000 times shorter than conventional accelerator lengths, promising a revolution in compactification and control. Much of this progress has been achieved using gaseous plasma targets and the beaming of the electrons is typically along the direction of the laser itself.
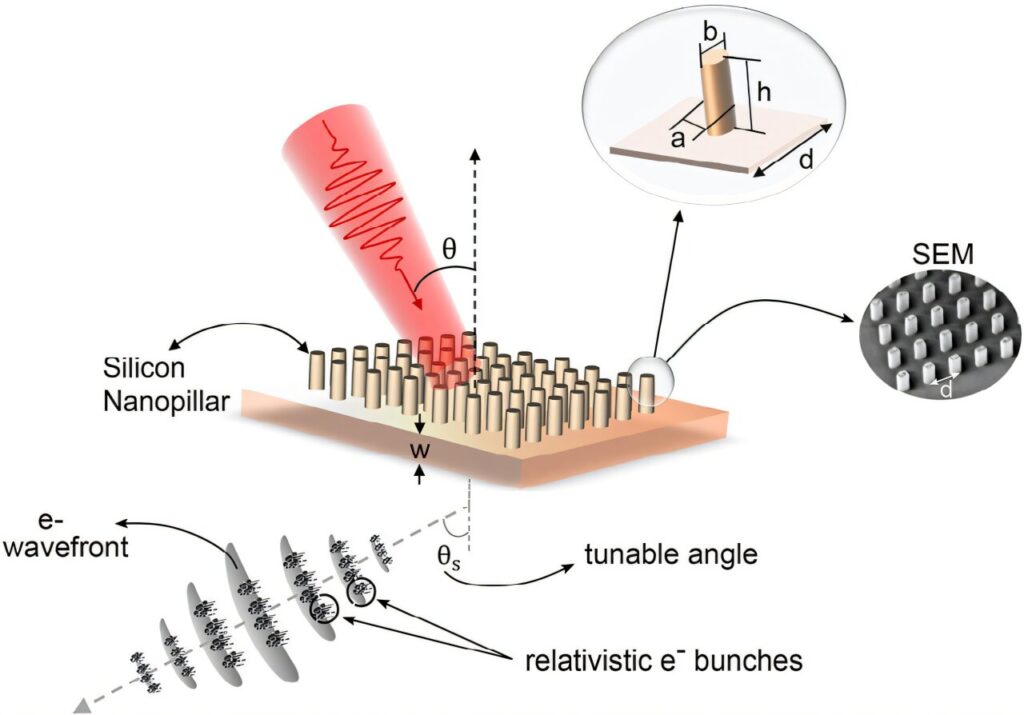
It is therefore imperative to find ways to get electrons at larger fluxes, say using a solid target, at the same time as controlling their directionality. For planar solids, the laser incident direction and polarization control the energies and the emission direction of the electrons. The beams are rather broad in their angular spread, getting even broader at higher laser intensities. Changing their direction or forming a narrow beam are extremely difficult challenges.
This is precisely where the present advance steps in. Using a solid with a surface decorated by nanopillars, the authors drive MeV energy pulses of electrons and steer them in narrow beams by adjusting the laser incidence angle. The nanostructure enhances the local electric fields, providing higher acceleration than planar surfaces can, while a judicious choice of the incident angle and spacing can direct the electron pulses in a desired direction. A great bonus—simulations show that the electron pulses have attosecond duration.
In summary, ordered nano steps can not only give a mighty kick to electrons but also bunch them tightly in time and order them to travel in specified directions. The authors call this “plasma nanophotonics,” driving an analogy with an array of antennas- rightly spaced- emitting directional, coherent electromagnetic radiation.