Vaccines and therapies based on messenger RNA could be more readily delivered due to a non-toxic polymer that protects RNA and controls its release inside cells.
The advent of vaccines using messenger RNA (mRNA) to direct immunogenic protein synthesis, best-known in vaccines against COVID-19, is stimulating researchers to find better ways to keep the mRNA stable and deliver it effectively.
A team at the University of Tokyo, with collaborators in Japan and China, has now developed polymers that can interact with, stabilize and encase mRNA, allowing highly effective delivery into cultured human cells and cells of live mice. They have published their work in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
“Beyond vaccines for infectious diseases, mRNA presents promising avenues for unprecedented treatments like protein replacement therapies, gene editing, and immunotherapies,” says Horacio Cabral of the University of Tokyo team. “But to unlock the full potential of these advanced therapies, the development of safe and effective carrier systems is paramount.”
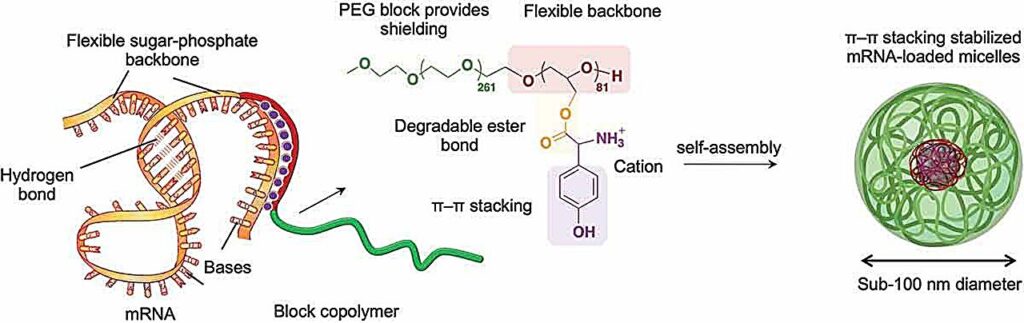
The researchers investigated ways to fine-tune the structure of their polymer molecules to allow them to interact with mRNA to protect it. The biocompatible and non-toxic polymers were of a type called block-copolymers, built from alternating segments of different chemical groups, in this case polyethylene glycol and polyglycerol.
But the key to achieving appropriate interaction with mRNA was to attach specific positively charged amino acid groups to the long polymer backbone. The positive charge generally attracts the polymer to negatively charged RNA, and the chosen amino acids were also able to interact with parts of the mRNA in a process called pi–pi (π–π) stacking. This involves interactions between electrons in a feature called pi bonds in cyclic molecular rings stacked side by side in the interacting molecules.
“This is a highly customizable approach, allowing fine-tuning of our polymer’s interactions with mRNA,” says Cabral. As a result, the mRNA was stabilized highly effectively, overcoming a major drawback of instability found with alternative approaches.
The polymer and mRNA spontaneously assembled into spherical bundles—micelles—that effectively delivered the mRNA cargo into cultured cells and also into mouse cells after intramuscular injection. The mRNA was readily released inside cells to generate the proteins it encoded at high efficiency, and for a significantly longer time than alternative approaches.
“This work was very challenging due to the delicate nature of mRNA, a highly fragile molecule that needs protection outside target cells but immediate exposure to the cell machinery once inside,” says Cabral. He adds, “Our success is exciting due to its potential to transform mRNA delivery technologies, allowing precise engineering, innovative release strategies, and overcoming critical barriers to enhance stability and efficacy in mRNA-based therapies.”