Recently, a research team led by Prof. Wu Zhengyan from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration Binzhou Medical University, successfully designed a nanostructure that improves the detection and treatment of tumors.
Their work, recently published in Small, focuses on creating a highly specific method for diagnosing and treating tumors using a combination of magnetic resonance imaging and enzyme activity.
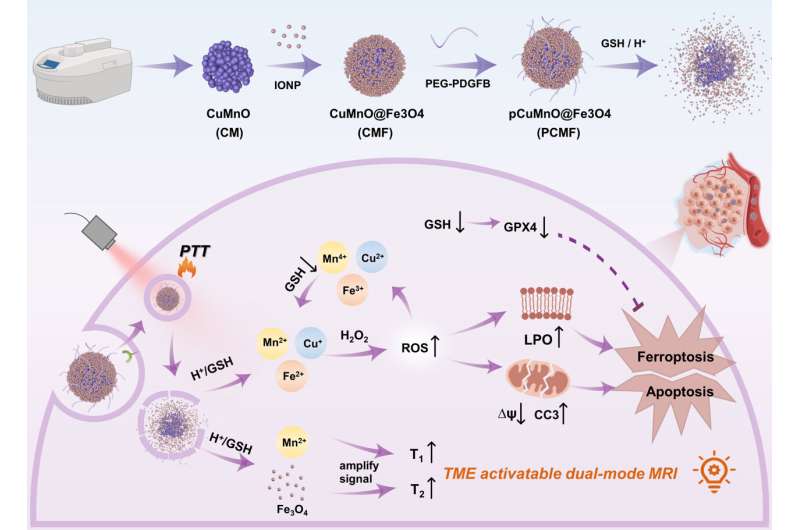
“Certain chemical reactions called the metal ion-mediated Fenton-like reaction, can quickly increase the levels of harmful reactive oxygen species and slow down tumor growth,” said Prof. Wu, “and enzymes made of copper, which have high catalytic activity and respond well to the tumor environment, are not very stable.”
Therefore, developing a tumor microenvironment-responsive core-shell nano-theranostic agent enables early tumor diagnosis and monitoring of treatment effectiveness and protects copper-based nanoenzymes from deactivation due to steric hindrance.
To address this problem, the research team developed a specialized nanoenzyme called CuMnO@Fe3O4 (CMF) with a core-shell structure that responds to the tumor microenvironment. They then attached PDGFB targeting ligands to the surface of CMF, creating a specific nanoenzyme for tumors known as PCMF.
The core-shell design of PCMF prevents interference from thiol groups found in large molecules during circulation in the bloodstream. This promotes the anti-tumor activity of PCMF.
PCMF exhibits both T1 and T2 dual-contrast imaging capabilities when activated by weak acid and glutathione. This means it can provide enhanced imaging contrast for diagnosing tumors.
Additionally, PCMF degrades in the tumor microenvironment, releasing metal ions as well as ultra-small iron oxide. This process consumes glutathione, accelerates Fenton and Fenton-like reactions, increases intracellular reactive oxygen species levels, and induces apoptosis and ferroptosis in cancer cells.
PCMF also possesses photothermal conversion capability and thus can be used for combined photothermal and nano-catalytic therapy, enhancing anti-cancer activity.
According to the team, this work provides insights into achieving highly sensitive tumor-specific therapeutic diagnosis.

