A team of researchers from the ITACA Institute of the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the Research Institute of Chemical Technology, a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the UPV, has discovered a new method for the manufacture of metal nanocatalysts that is more sustainable and economical.
With great potential in the industrial sector, the method would contribute to the decarbonization of industry. The work has been published in the journal ACS Nano.
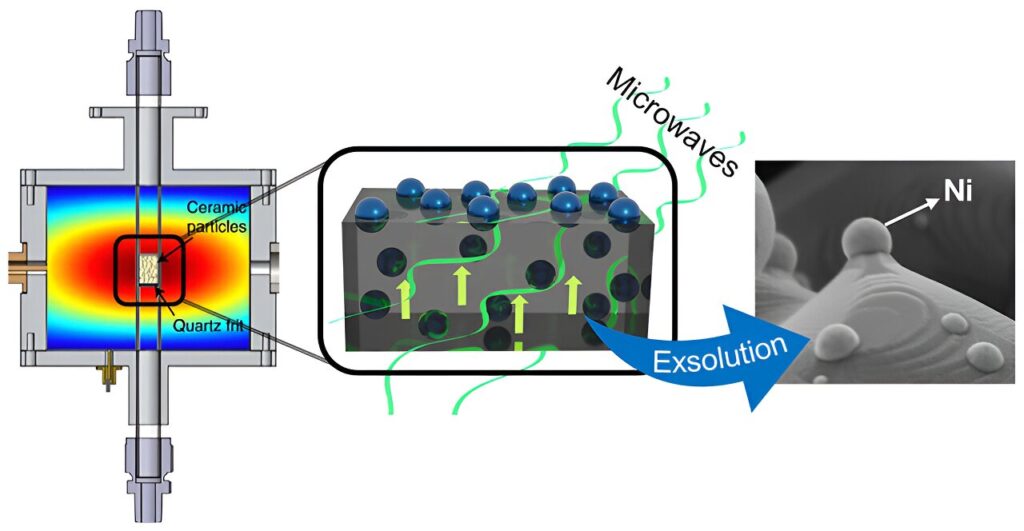
This new method is based on the exsolution process activated by microwave radiation. Exsolution is a method of generating metallic nanoparticles on the surface of ceramic materials. “At elevated temperatures and in a reducing atmosphere (usually hydrogen), metal atoms migrate from the structure of the material to its surface, forming metal nanoparticles anchored to the surface. This anchoring significantly increases the strength and stability of these nanoparticles, which positively impacts the efficiency of these catalysts,” explains Beatriz García Baños, a researcher in the Microwave Area of the ITACA Institute at the UPV.
In the study, the UPV and CSIC researchers have shown that thanks to microwave radiation, this process can be carried out at more moderate temperatures and without the need to use reducing atmospheres.
“In this way, active nickel nanocatalysts can be produced in a more energy-efficient exsolution process. These catalysts have been proven to be active and stable for the reaction of CO production from CO2, obtaining a product of industrial interest and contributing to the decarbonization of the sector,” says Alfonso Juan Carrillo Del Teso, researcher of the Energy Conversion and Storage Group of the ITQ.
The exsolution process demonstrated in nickel nanoparticles has been carried out at temperatures of about 400ºC and exposure times of a few seconds, whereas the conventional exsolution procedure in these materials occurs at temperatures of 900ºC, with times of about 10 hours. In addition, this technology allows exsolution to be performed without using hydrogen.
“For all these reasons, we improve the sustainability of the process. Moreover, by obtaining the catalysts at milder temperatures and shorter exposure times, we reduce the costs of the process, which is also influenced by not having to use hydrogen as a reducing gas,” adds Beatriz García Baños.
Applications
The process developed by the UPV and CSIC team is primarily intended for high-temperature catalytic procedures for storing and converting renewable energy. It could also be applied to biogas reforming reactions for the production of synthesis gas (precursor of liquid fuels), CO2 hydrogenation reactions applicable to Power-to-X systems, and functionalizing electrodes for fuel cells and/or high-temperature electrolyzers.
Provided by
Universitat Politècnica de València