Often overlooked, rechargeable batteries play an important part in contemporary life, powering small devices like smartphones to larger ones like electric vehicles. The keys to creating sustainable rechargeable batteries include having them hold their charge longer, giving them a longer life with more charging cycles, and making them safer. Which is why there is so much promise in all-solid-state batteries.
The problem is discovering which solid electrolytes offer such potential advantages.
In a step toward that goal, an Osaka Metropolitan University research group led by Assistant Professor Kota Motohashi, Associate Professor Atsushi Sakuda, and Professor Akitoshi Hayashi of the Graduate School of Engineering has developed an electrolyte with high conductivity, formability, and electrochemical stability.
The findings were published in Chemistry of Materials.
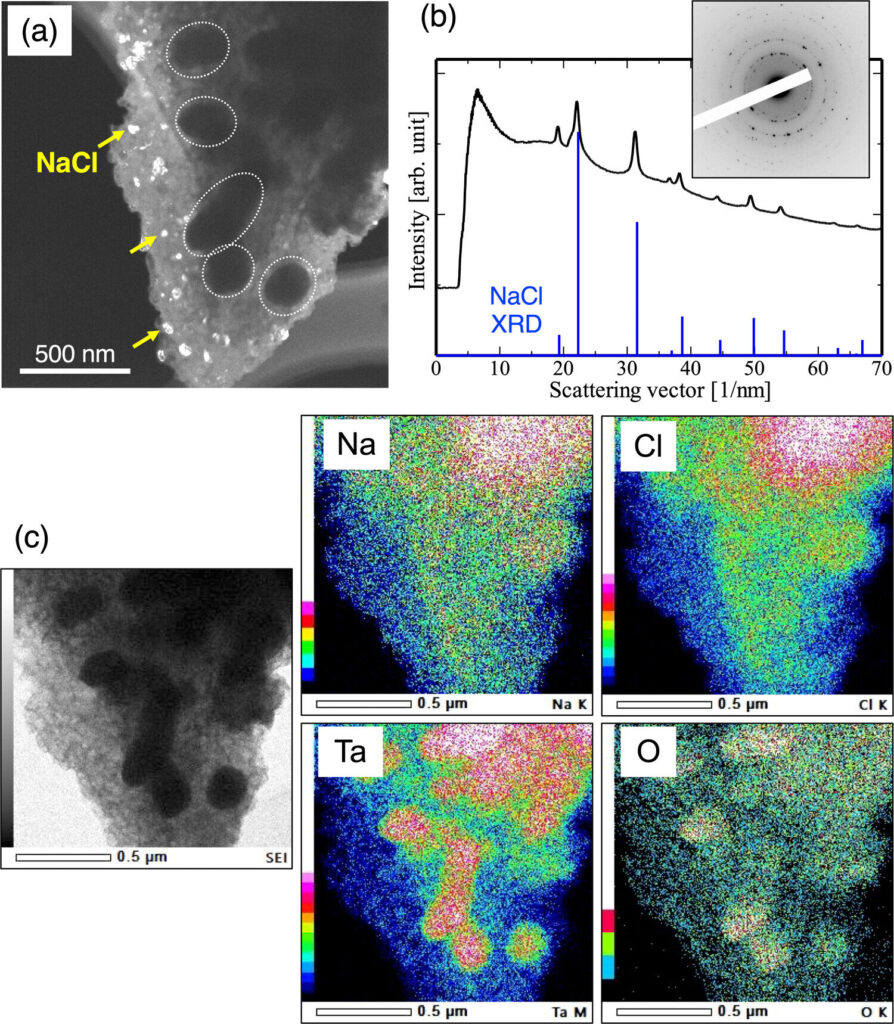
The group achieved high conductivity at room temperature by adding Ta2O5 (tantalum pentoxide) to the previously developed solid electrolyte NaTaCl6, a combination of tantalum chloride and sodium chloride.
The discovered solid electrolyte, Na2.25TaCl4.75O1.25, also has a higher electrochemical stability than conventional chlorides and superior mechanical properties.
“The results of this research are expected to make a significant contribution to the development of composite solid electrolytes, in addition to the glass and crystal solid electrolytes that have been developed to date,” Professor Motohashi suggested.
“We will now be focusing on elucidating the ionic conduction mechanism of composite solid electrolytes and further developing materials.”