U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) scientists confirm the identification of a new class of semiconductor nanocrystals with bright ground-state excitons, a significant advancement in the field of optoelectronics, in an article published in the American Chemical Society (ACS) journal ACS Nano.
The groundbreaking theoretical research could revolutionize the development of highly efficient light-emitting devices and other technologies.
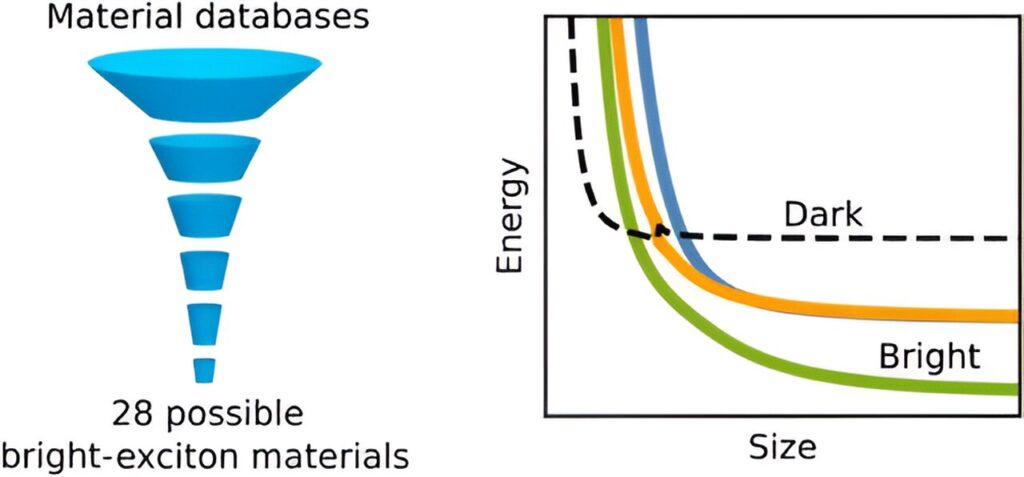
Generally, the lowest-energy exciton in nanocrystals is poorly emitting, earning the name “dark” exciton. Because it slows the emission of light, the dark exciton limits the performance of nanocrystal-based devices like lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Scientists have long sought to overcome the dark exciton.
“We set out to find new materials in which the exciton ordering is inverted, so that the lowest-energy exciton is bright,” said John Lyons, Ph.D., from the Theory of Advanced Functional Materials Section. “Searching through open-source databases of materials using criteria informed by our theoretical modeling, we identified over 150 targets. We further narrowed this list with advanced first-principles calculations, ending up with 28 candidates for bright-exciton nanomaterials.”
More detailed modeling of these materials indicates that at least four can yield bright ground-state excitons in nanocrystals. “This discovery, made in collaboration with Prof. David Norris from Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich and Peter Sercel, Ph.D., from the Center for Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Semiconductors for Energy (CHOISE), could pave the way for the development of ultrabright and highly efficient light-emitting devices, lasers, and other technologies,” Lyons said.
Alexander Efros, Ph.D., a senior scientist, Materials Science division and the senior author on the paper, elaborated on the implications of the research.
“In our research, we have identified several bright-exciton materials that can emit light across a broad spectrum, from infrared to ultraviolet,” said Efros. “This versatility makes them very useful for optoelectronic applications. The capability to engineer nanocrystals with bright excitonic states across this wide range opens new avenues for creating better and more efficient LEDs, solar cells, and photodetectors.”
By resolving the dark-exciton problem, NRL scientists hope to stimulate the large nanomaterial community to attack bright-exciton nanostructures, an area that has been stalled for too long. Today, three of these materials are being grown at NRL as part of the Nanoscience Institute Program’s Bright Nanocrystal Emitters initiative aiming to conclusively demonstrate bright-exciton behavior in the lab and leverage it for future naval technologies.
“Our findings demonstrate the power of combining high-throughput computational screening, pen-and-paper theory, and high-accuracy calculations of electronic structure,” said Michael Swift, Ph.D. “No one technique would be enough on its own, but together we discovered new ultrabright nanocrystals and unlocked the power of the bright exciton across unexplored classes of materials.”
The Theory of Advanced Functional Materials Section performs basic and applied research on functional, structural, biological, and electronic materials systems. The section pioneers new methods for simulating materials and systems, including original development of computational and theoretical techniques, modification of existing approaches, and application of established methodologies to new materials and areas. The goal of the section is to use theory and simulation to understand, improve and develop materials of present and future naval importance.